So, what is a Trojan virus? Think of the legendary Trojan Horse from Greek mythology, but redesigned for your digital life. It’s a sneaky type of malware that disguises itself as a legitimate program – like a free game, a helpful PDF converter, or an important software update – to trick you into willingly letting it through your computer’s defenses.
This isn’t just a far-off tech concept; it’s a very real threat that could be targeting your device right now. Trojans are the master keys hackers use to steal banking information, spy on your private conversations, and take complete control of your digital world, often without you suspecting a thing until it’s too late.
With years of experience analyzing malware behavior, I’ve seen countless users become victims simply because they downloaded a file that seemed harmless. Understanding how to spot these deceptions isn’t just for tech experts; it’s a fundamental survival skill for everyone online today.
In this comprehensive guide, I will break down everything you need to know:
- What a Trojan is and exactly how it operates.
- The key differences between a Trojan and a traditional virus are.
- The most common types you need to watch out for.
- How to detect, remove, and ultimately protect yourself from this threat.
Don’t let a clever disguise be the downfall of your online security. Let’s get you armed with the knowledge to defend your digital life.
1. What is a Trojan virus?
You’ve probably heard the ancient Greek legend of the Trojan War. After a long siege, the Greeks pretended to sail away, leaving behind a massive wooden horse as a supposed gift for the city of Troy. The Trojans, celebrating their victory, pulled the “gift” inside their walls. Under the cover of night, Greek soldiers hiding inside the horse emerged, opened the city gates, and conquered Troy.
In the digital world, this ancient tactic has a modern and far more personal counterpart. A Trojan is a type of malware that hides inside a program or file that seems legitimate and useful. It could be disguised as a free photo editor, an important document, a software update, or even a funny video.

The critical part of this attack is that you, the user, willingly run the program, effectively pulling the “horse” inside your own digital walls. Unlike a virus, a Trojan doesn’t replicate itself. It relies entirely on deception to get you to install it.
This isn’t just theoretical. At Safelyo, we’ve seen countless cases where users accidentally installed a Trojan simply because it was bundled with a ‘free PDF converter’ or a ‘game crack’ they downloaded from an untrusted source. It’s a digital bait-and-switch, and your data is the prize.
2. Trojan vs. Virus: Clearing up the key confusion
It’s one of the most common mix-ups in cybersecurity, so let’s set the record straight: Is a Trojan a virus or malware? The simple answer is that a Trojan is a type of malware, but it is not technically a virus.
The single biggest difference comes down to one thing: self-replication.
A computer virus, much like its biological namesake, is designed to spread. It attaches itself to legitimate files or programs and automatically self-replicates, infecting other files on your computer and potentially spreading to other systems without your direct help.
A Trojan, on the other hand, is a standalone program that cannot replicate itself. It’s like a spy in disguise; it needs to trick you into inviting it into your system. Once you run the malicious program, the Trojan gets to work, but it won’t start copying itself onto your other files. Its main job is often to open a “backdoor” to let other malware in, which could include viruses.
To make it even clearer, here’s a simple breakdown:
| Feature | Trojan | Virus |
|---|---|---|
| How it Spreads | Tricks the user into installing it (social engineering). | Attaches to other files and self-replicates automatically. |
| Self-Replication | No, it cannot copy itself. | Yes, this is its primary function. |
| Main Purpose | To create a backdoor, steal data, or deliver other malware. | To spread, corrupt files, and disrupt system operations. |
| Analogy | A spy in disguise was invited into a castle. | A contagious cold that spreads from person to person. |
So, while both are dangerous forms of malware, how they infect your system is fundamentally different.
3. How do Trojan viruses infect your devices?
Trojans don’t just appear out of thin air. They rely on clever psychological tricks and deceptive tactics to get you to lower your guard. From my years of analyzing cyber threats, I’ve seen that nearly all infections boil down to a moment of misplaced trust. Let’s break down the most common ways these digital con artists find their way onto your computer.
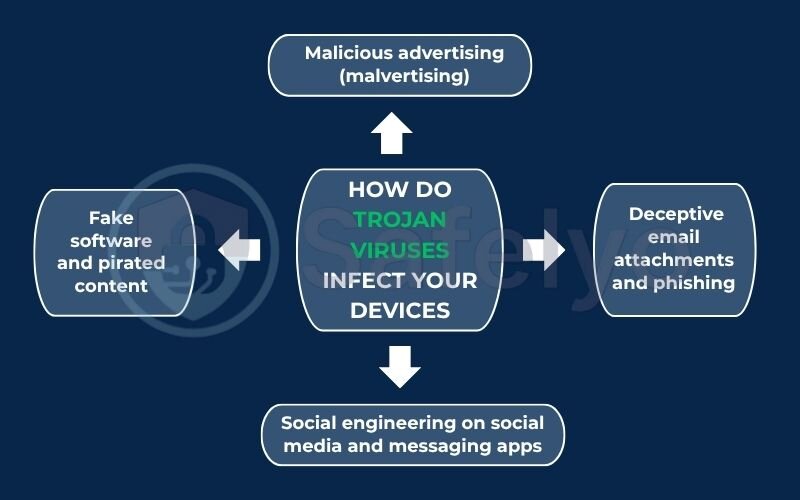
3.1. Deceptive email attachments and phishing
This is the oldest trick in the book, and it still works. You receive an email that looks like it’s from a legitimate company – like FedEx, Amazon, or your bank. It might contain an “invoice,” a “shipping notification,” or a “security alert.” The goal is to make you panic and click before you think.
For instance, a common scam involves an email that looks like it’s from FedEx with an attachment named invoice.zip. When you open it, you aren’t greeted with an invoice. Instead, you’ve just silently run a Trojan installer. My advice is always to be suspicious of unsolicited attachments, even if they look official.
3.2. Fake software and pirated content
The lure of getting something for free is a powerful one, and hackers know it. They host Trojans on websites offering “cracked” versions of expensive software, video games, or activation tools (keygens).
Imagine you’re searching for a free version of Adobe Photoshop. You find a shady website, download the file, and run the installer. The software might even appear to work, but in the background, you’ve also installed a Trojan that now has access to your system. I always tell people: if you aren’t paying for the product, you are the product.
3.3. Malicious advertising (malvertising)
You can get infected even without downloading anything intentionally. Hackers can inject malicious code into advertisements on otherwise legitimate websites. These ads often use scare tactics, flashing warnings like “Your computer is infected! Scan now!”
When you click the ad, it either redirects you to a malicious site or triggers a “drive-by download,” installing the Trojan without any further action from you. This is particularly tricky because it can happen on sites you visit and trust every day.
3.4. Social engineering on social media and messaging apps
Hackers exploit the trust you have in your social circles. A classic example I see frequently is a message on Facebook or WhatsApp from a friend’s account (which has likely been hacked) that says something like, “OMG, did you see this video of you?” with a suspicious link.
Curiosity gets the better of you, you click the link, and you’re prompted to install a “video player update” to see it. That “update” is the Trojan. If a message seems out of character, even from a friend, it’s always worth sending a separate message to verify they actually sent it.
4. Telltale signs of a Trojan infection on your device
Unlike a loud, crashing virus, a Trojan often tries to stay hidden. However, it’s hard to operate in the shadows without leaving a few clues. Your computer might be trying to tell you something is wrong.
From my experience helping people troubleshoot their devices, the very first complaint is almost always the same: “My computer just got really slow out of nowhere.” It’s often a sign that a malicious process, like a Trojan, is secretly hogging your system’s resources in the background.

Keep an eye out for these other red flags:
- Your computer becomes sluggish. Tasks that were once instant now take forever. You might hear the cooling fan spinning loudly even when you’re not doing anything demanding. This is your computer working overtime on a hidden task.
- You see strange pop-ups. These aren’t normal website ads. They are often for questionable products or services and may appear even when your web browser is closed.
- Your browser settings have changed. Suddenly, your homepage is a weird search engine you’ve never heard of, or your default search provider has been swapped. This is a classic browser hijacking symptom.
- Unfamiliar toolbars appear. You open your browser to find that new, mysterious toolbars have been added without your permission.
- Your antivirus program is disabled. This is a massive red flag. Sophisticated Trojans will often try to disable your security software first to ensure they can operate freely.
- There’s a spike in internet activity. You notice your internet connection is unusually slow, or the activity light on your router is blinking frantically even when you aren’t actively using the internet. The Trojan could be sending your data to a remote server.
- Your online accounts are acting strangely. You might get locked out of your email, or friends tell you they’ve received spam messages from your social media account that you didn’t send.
5. The most common types of Trojan malware you should know
“Trojan” is a broad category. Think of it like the word “car” – there are sports cars, SUVs, and pickup trucks, each designed for a different purpose. Trojans are similar, with specialized types built to carry out specific malicious jobs. Understanding these types helps you grasp the real danger they pose.
Here’s a quick summary of what each one does:
| Trojan Type | Main Goal |
| Backdoor Trojan | Gives hackers remote control of your PC. |
| Banking Trojan | Steals online banking & credit card info. |
| DDoS Trojan | Uses your PC to help attack websites. |
| Downloader Trojan | Downloads and installs more malware. |
| Ransom Trojan | Locks your files and demands money. |
| Spy Trojan | Records your activity (keystrokes, webcam). |
Let’s look at the most common variants you’re likely to encounter.
5.1. Backdoor Trojan
As the name suggests, this Trojan creates a secret “backdoor” into your computer. It allows a hacker to remotely access and control your device, bypassing all normal security measures.
It’s like giving a burglar a secret key to your house. They can come and go as they please, steal your belongings, install surveillance cameras (spyware), or even use your house as a base for other crimes without you knowing.
5.2. Banking Trojan (e.g., Zeus)
This is one of the most financially damaging types. It’s specifically designed to steal your online banking credentials, credit card numbers, and other financial data.
This is a digital pickpocket that stands over your shoulder when you’re at a virtual ATM. It waits for you to type in your username and password on your bank’s website and then records that information to drain your account later.
5.3. DDoS (distributed denial-of-service) Trojan
This Trojan turns your computer into a “zombie” or “bot.” It doesn’t harm your computer directly, but uses its internet connection to participate in a coordinated attack against a specific website or online service, overwhelming it with traffic until it crashes.
Imagine a single person being hired to shout at a storefront. Now imagine a Trojan hiring your computer and thousands of others to all shout at the same storefront at once. The store’s owner can’t serve real customers because of the noise. Your computer is now part of a mob, often without you even realizing it.
5.4. Downloader Trojan
This Trojan’s primary mission is simple: once it’s on your system, its job is to download and install other types of malware.
This is the scout that breaches the castle walls first. Its only job is to open the main gate to let the entire invading army (viruses, ransomware, spyware) rush in behind it.
5.5. Ransom Trojan
This type of Trojan functions like ransomware. It encrypts your important files – documents, photos, videos – making them completely inaccessible. It then displays a message demanding you pay a ransom (usually in cryptocurrency) to get the decryption key.
It’s a digital kidnapper. It doesn’t steal your photos; it locks them in a safe and then sells you the combination.
5.6. Spy Trojan (spyware)
This Trojan is designed to spy on you. It can log every keystroke you make (a keylogger), take screenshots of your activity, access your webcam and microphone, and steal your saved passwords.
This is a private investigator hired to watch your every move. It hides in your home, records everything you say and do, and reports it all back to the person who hired it. It’s a total invasion of your privacy.
Read more:
6. Real-world examples of infamous Trojan attacks
These threats aren’t just theoretical. Over the years, specific Trojans have become infamous for the sheer scale of their damage, costing individuals and businesses billions of dollars. Learning from history helps us understand just how serious these attacks can be. As someone who has tracked these threats for years, a few names always stand out.
Zeus (or Zbot): The King of Banking Trojans
If there was ever a celebrity in the malware world, it’s Zeus. First appearing in 2007, Zeus pioneered the art of stealing online banking information. It infected millions of computers worldwide through phishing emails and drive-by downloads. Once on a system, it would patiently wait for the user to visit a banking website and then secretly record their login details. It’s estimated that the Zeus botnet was used to steal hundreds of millions of dollars, making it one of the most successful pieces of financial malware ever created.
Emotet: More Than Just a Trojan
Emotet is a perfect example of a Trojan that acts as a “downloader.” It started as a banking Trojan but evolved into one of the most dangerous malware delivery services on the planet. I remember security communities calling it the “Swiss Army knife” of malware. Getting infected with Emotet was just the beginning; it would then download other devastating payloads, such as ransomware that would lock up entire hospital and government networks. Its ability to spread rapidly and deliver other threats made it a global cybersecurity nightmare for years.
Backdoor.Ratsauce: The Modern Spy
This is a more recent example that shows these threats are constantly evolving. Backdoor.Ratsauce was used in targeted espionage campaigns, often delivered via highly convincing phishing emails. Once inside, it didn’t steal money or lock files. Instead, it operated like a true spy, quietly collecting sensitive documents, recording conversations, and sending everything back to its controllers. It highlights that the goal isn’t always financial; sometimes, it’s about stealing information and secrets.
See also:
7. FAQ about the Trojan virus
We’ve covered a lot of ground, but you might still have a few specific questions. Here are some quick, direct answers to the most common queries we see about Trojans.
What does a Trojan virus do?
A Trojan’s goal depends on its type. Its main jobs are typically to steal sensitive information (like banking passwords), give a hacker remote control of your computer, lock your files for ransom, spy on your activity, or download even more dangerous malware onto your device.
How do I tell if I have a Trojan virus?
The most common signs are your computer suddenly running very slowly, frequent pop-up ads, your browser homepage changing without your permission, and your antivirus software being mysteriously disabled. For a full list, check the “Telltale signs” section above.
How serious is a Trojan virus?
A Trojan can be extremely serious. Depending on its type, it can lead to complete financial loss through banking theft, identity theft if your personal data is stolen, permanent data loss from ransomware, and a total invasion of your privacy.
How do I get rid of a Trojan virus?
The most reliable way is to use a strong antivirus program and run a full system scan. The manual process involves disconnecting from the internet, rebooting into Safe Mode, and uninstalling suspicious programs, as detailed in our step-by-step guide earlier.
Is a Trojan virus warning real?
This is a tricky one. Pop-up warnings that appear in your web browser are almost always scams designed to trick you into downloading fake security software (which is often a Trojan itself). However, a warning that comes directly from your trusted, installed antivirus software is very real and should be taken seriously.
Can a Trojan infect Macs and mobile phones?
Yes. While they are far more common on Windows computers, Trojans absolutely exist for both macOS and Android devices. They often disguise themselves as fake apps in third-party app stores or spread through phishing links sent via text or email.
Can Windows Defender remove Trojans?
Windows Defender (now Microsoft Defender) has become quite capable of detecting and removing many common Trojans. However, for complete peace of mind against newer and more sophisticated threats, a dedicated, premium antivirus solution is often recommended as it has more advanced features and is updated more frequently.
What is the most famous Trojan horse virus?
Zeus (or Zbot) is one of the most infamous banking Trojans in history. It infected millions of computers and was used to create a massive botnet that stole hundreds of millions of dollars by capturing online banking credentials.
8. Conclusion
Understanding what is a Trojan virus moves it from a scary, unknown concept to a preventable threat. The real power of a Trojan isn’t in its complex code, but in its simple ability to trick you. By being aware of its disguises, you’ve already won half the battle.
To keep your digital life secure, always remember these key points:
- Trojans disguise themselves as legitimate files and programs to fool you.
- They are different from viruses because they don’t self-replicate; you have to run them.
- Vigilance is your first line of defense – be skeptical of unsolicited attachments and downloads.
- A reliable antivirus is your essential safety net for catching what you might miss.
Cybersecurity is a continuous process, not a one-time fix. Stay alert and stay protected. Now that you understand the threat, take the next step to secure your devices. See Safelyo expert picks for the best antivirus software in our Antivirus category to find the perfect shield against Trojans and other malware.