Does VPN slow down internet is one of the very first questions that pops into most people’s minds when they’re thinking about using, or already using, a virtual private network. While these services are champions for online safety, the worry about a sluggish connection is understandable.
I’ve spent years testing and tinkering with all sorts of tech, and I can tell you that a VPN can add a little drag to your connection speed. But here’s the good news: it’s not always a dramatic slowdown, and there’s plenty you can do about it.
In this guide, we’ll break down:
- The real reasons why a VPN might be tapping the brakes on your connection.
- Simple, effective ways to get that speed back up.
- How to pick a VPN that’s built for speed without skimping on security.
So, don’t let speed fears put you off. Let’s dive in and figure out how to make your VPN experience both safe and speedy.
1. Does VPN slow down internet?
The short answer: Yes, a VPN can slow down the internet, but it's not always significant.
Let’s get straight to the point: YES, a VPN can slow down the internet connection. There’s no magic trick to avoid this entirely. Think of it like adding an extra, very secure checkpoint for your data to pass through. Your information gets encrypted (scrambled for safety), sent to the VPN server, then decrypted (unscrambled), and finally sent on to its destination. This extra work naturally takes a little more time.
However, the key thing to understand is that the impact a VPN has on internet connection isn’t always a deal-breaker. For many everyday tasks like browsing, emailing, or even streaming standard-definition video, you might barely notice the difference, especially if you’re using a quality VPN service. The actual drop in speed can vary wildly – sometimes it’s a tiny blip, other times it can be more noticeable.

From my own experience, I’ve seen reductions range from almost imperceptible to quite significant. The top-tier services, however, often manage to keep you running at 70-80% or even more of your original performance. A slowdown is possible, but it’s a small price for the security a VPN offers. Fortunately, there are many ways to minimize this impact.
>> Read more:
2. Why does a VPN slow down the internet?
So, we’ve established that a VPN can put the brakes on your internet speed. But why exactly does a VPN slow down the internet? It’s not just one single culprit, but rather a combination of factors all working together. Understanding these can help you pinpoint potential issues and, more importantly, figure out how to address them. Let’s break down the main reasons.
2.1. Encryption and decryption overhead
At the heart of every VPN is encryption. This is the process of scrambling your data packets so that no one, not your internet service provider (ISP), hackers, or snoops, can read them.
When your data arrives at the VPN server, it must be decrypted so it can reach the website or service you want to use. The returning information is then encrypted again by the server and decrypted once more on your device. This ongoing cycle of securing and decoding information consumes CPU and RAM resources on both your device and the server.
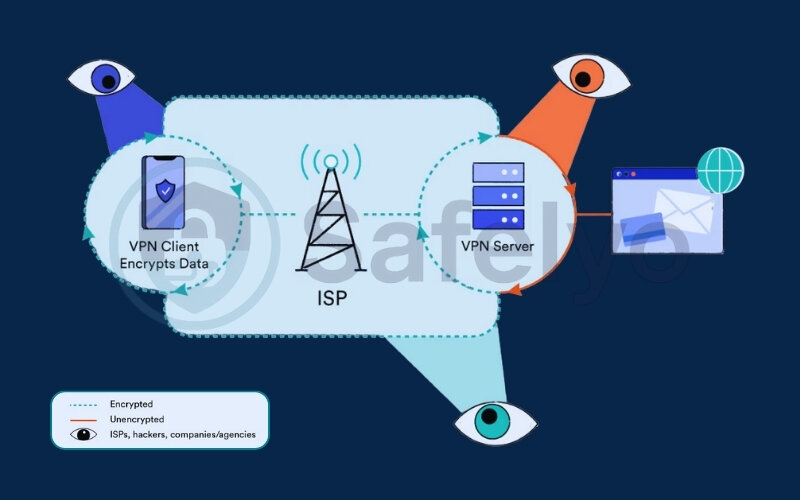
Think of it like this: Imagine you’re sending a secret message. First, you have to write it in code (encryption), then your friend has to decipher it (decryption). If the code is complex (stronger security), it takes more time and effort for both of you.
Stronger encoding levels, like AES-256 (which is excellent for security), naturally create a bit more overhead than lighter ones, though modern devices handle this pretty efficiently. Still, it’s a fundamental step that adds a tiny delay.
2.2. Distance to the VPN server
Geography plays a surprisingly big role in your VPN speed. When you connect to a VPN, your internet traffic doesn’t go directly to the website you want to visit. Instead, it first travels to the VPN server you’ve selected, and then from that server to your final destination. The reverse happens for data coming back to you.
Naturally, the further your data has to physically travel, the longer it will take. This delay is known as latency. Connecting to a distant server will cause a slower connection and higher ping. Connecting to a nearby server is almost always faster. This directly impacts the VPN server’s distance speed.
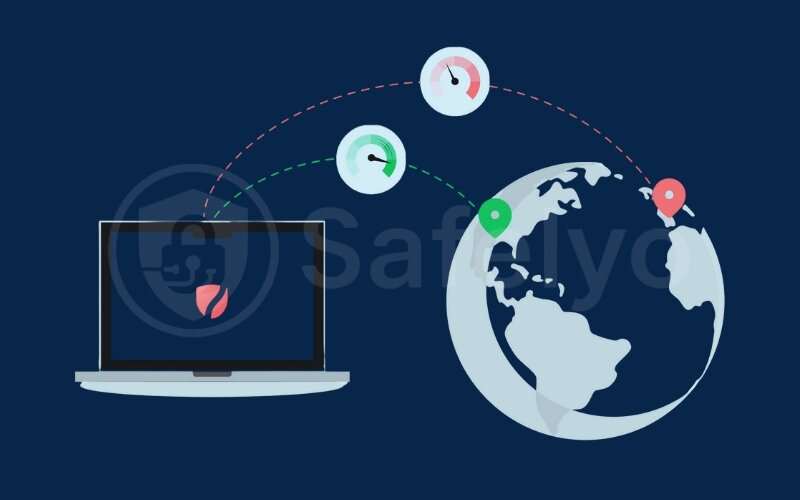
For example, if you’re in Vietnam and connect to a VPN server in New York, your data is making a very long round trip. Expect a slower response time compared to connecting to a server in Singapore.
In my tests, I consistently find that choosing a server geographically closer to my actual location yields significantly better speed results. It’s one of the first things I check when troubleshooting a slow VPN.
>> You may also be interested in: The fastest VPN in 2026 (with hard data on speed tests)
2.3. VPN server load and quality
Not all VPN servers are created equal, and how busy they are matters a lot.
First, let’s talk about server load. If a particular server has too many users, it can lead to server congestion, and its resources get stretched thin. Think of it like a highway during rush hour – more cars mean slower traffic for everyone. This is a common reason for slowdowns, and it’s one of the key factors affecting VPN speed.
Second, the quality of the server hardware and its internet connection is crucial. A high-quality VPN provider invests in powerful servers with fast connections (e.g., 1 Gbps or even 10 Gbps ports) and robust network infrastructure. Lower-tier or, notoriously, free VPNs often use cheaper, less powerful servers that can easily become overwhelmed, leading to poor VPN performance impact.
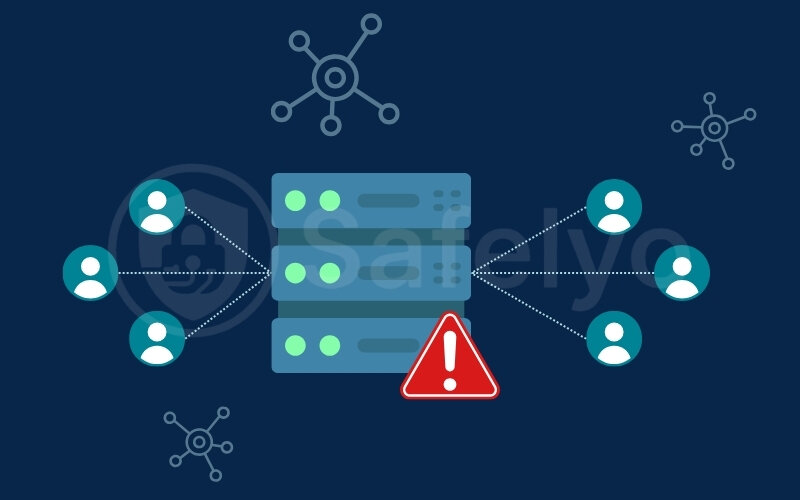

This is a classic “you get what you pay for” scenario. Many free VPNs slow down your internet because they rely on underpowered or overcrowded servers that can’t keep up with demand.
Furthermore, it’s not just about user load. Beyond server load from user numbers, some providers, especially free VPNs, might impose VPN bandwidth limits on their servers, or the servers themselves have connection ports (e.g., 1 Gbps) insufficient to meet high demand. This artificial cap, or simply an under-provisioned server, will directly throttle your speed regardless of how few users are connected.
In my work helping individuals and small teams implement VPNs for secure remote access, I’ve often encountered the same concern: Why is my internet slower after turning on the VPN? In one particular case, a client was using a free VPN and unknowingly connected to a highly congested server overseas. After switching to a nearby premium server with proper load balancing, their speed improved dramatically. That experience made it clear: VPN speed isn’t just about having a VPN, it’s about using the right infrastructure behind it.
2.4. VPN protocol in use
The VPN protocol is essentially the set of rules and instructions that your device and the VPN server use to establish a secure connection. Different VPN protocols offer varying balances between speed, security, and reliability. The choice of protocol can have a noticeable impact on your connection speed.
Some common VPN protocols include:
WireGuard
This is a relatively new protocol that has quickly gained popularity for being lightweight and extremely fast, often considered the fastest VPN protocol currently available. It generally provides excellent security as well.
OpenVPN
A very popular and highly secure open-source protocol. It can run over UDP (User Datagram Protocol) or TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). OpenVPN UDP is generally faster than TCP because it has less error correction, while OpenVPN TCP is more reliable for ensuring data delivery, though a bit slower.
IKEv2/IPSec
(Internet Key Exchange version 2/Internet Protocol Security)
Known for its stability and speed, especially on mobile devices, as it’s good at reconnecting if your internet connection drops momentarily.
Experimenting with different protocols within your VPN application’s settings can sometimes lead to a significant speed boost. Many VPN apps allow you to easily switch between available protocols, so it’s worth trying them out to see which one performs best for your specific network and needs.
2.5. Your baseline internet speed from your ISP
This might seem obvious, but it’s a crucial point: A VPN cannot magically make your internet faster than what you’re paying your internet service provider (ISP) for. Your VPN connection speed is fundamentally limited by your existing internet plan.
If your base internet speed is slow to begin with, using a VPN will likely make it feel even slower, as any percentage decrease will be more noticeable. For instance, “if your internet plan only provides 30Mbps download speed, even the fastest VPN in the world won’t get you to 100Mbps.” The VPN is an overlay on your existing connection; it doesn’t replace or upgrade it.
The silver lining? The faster your baseline internet speed, the less impact you’ll likely feel from a VPN. If you have a gigabit connection, a 10-20% drop in speed might still leave you with ample data capacity for smooth browsing, streaming, and downloading. So, before blaming the VPN entirely, it’s worth knowing what your starting point is.
3. How to test your VPN speed accurately
Okay, so you suspect your VPN might be slowing things down, or maybe you’re just curious. The best way to know for sure how much a VPN affects your internet speed is to test it. Simple speed tests give you concrete numbers about your connection. This helps you decide if the performance is acceptable or if you should try our optimization tips.
Establish your baseline speed > Test with the VPN connected > Test multiple servers and protocols
It’s all about comparing your internet speed with VPN vs without. Here’s a straightforward approach to test VPN speed effectively:
3.1. Establish your baseline speed
First things first, you need a starting point.
- Disconnect your VPN: Make sure your VPN is completely turned off.
- Use a reliable speed test tool: Popular and generally dependable options include Speedtest.net by Ookla or Fast.com (powered by Netflix, good for checking streaming speeds).
- Run the test: Let it complete fully.
- Record the key metrics:
- Ping (ms): This is latency, or the travel time for data packets from your device to the test server and back. Lower is better.
- Download speed (Mbps/Gbps): How quickly you can pull data from the internet to your device. Higher is better.
- Upload speed (Mbps/Gbps): How quickly you can send data from your device to the internet. Higher is better.
This is your baseline internet speed – what your ISP is delivering without any VPN interference.
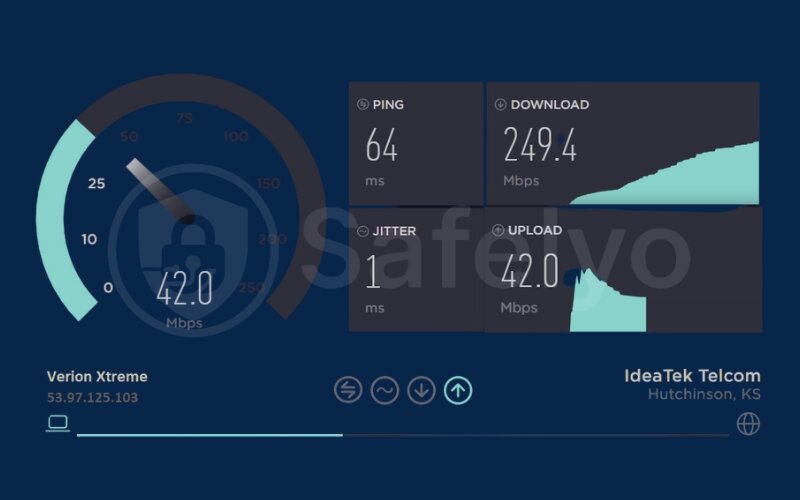
3.2. Test with the VPN connected
Now, let’s see what happens with the VPN active.
- Connect your VPN: Turn on your VPN and connect to your desired server region. If you usually connect to a specific server (e.g., “US – New York” or “UK – London”), use that one for a realistic test.
- Use the same speed test tool: Consistency is key for accurate comparison.
- Run the test again: Let it complete.
- Record the new metrics: Note down the ping, download speed, and upload speed with the VPN active.
Now you can directly compare the “before VPN” and “after VPN” results and see the difference.
3.3. Test multiple servers and protocols
To get a fuller picture, don’t stop at just one test.
- Test different server locations: If your VPN offers multiple servers in different cities or countries, try testing a few. You might find that some servers perform significantly better than others.
- Experiment with VPN protocols: As we discussed earlier, different protocols can yield different speeds. If your VPN app allows it, switch between protocols (e.g., WireGuard, OpenVPN UDP, IKEv2) and re-run the speed test on your preferred server location.
Here are a few tips from me for more accurate testing:
- Run tests multiple times and at different times of the day. Internet speeds can fluctuate due to network congestion, so an average over several tests gives a more reliable picture.
- Close other background applications that might consume data capacity. Ensure no one else is heavily using the internet in your household (streaming 4K movies, large downloads, online gaming) while you’re testing, as this can skew results.
- For maximum consistency, use the same test server on Speedtest.net (if it allows you to choose) for both your baseline and VPN tests. This eliminates a variable in the testing equation.
By following these steps, you’ll get a much clearer understanding of how your VPN is performing.
4. How to minimize VPN speed reduction and boost performance
A VPN can introduce some slowdown, but this speed loss is often manageable. In many cases, you can significantly fix or lessen the impact of a slow VPN. The substantial benefits a VPN offers in terms of security, and access to content usually make a slight, optimizable dip in speed a worthwhile trade-off.
Thankfully, you’re not powerless here. There are several effective strategies you can employ for optimizing connection speeds.
Before we dive deep into each method, here’s a quick rundown of what we’ll cover:
- Choose a closer server: Distance matters.
- Pick a less crowded server: Avoid digital traffic jams.
- Switch VPN protocols: Some are built for speed.
- Use a wired connection: More stable than Wi-Fi.
- Restart your gear: The classic IT fix.
- Temporarily disable conflicting software: For testing purposes.
- Consider an internet plan upgrade: If your baseline is too slow.
- Steer clear of unreliable free VPNs: They often come with speed (and security) costs.
- Use split tunneling: Route only specific traffic through the VPN.
Now, let’s explore each of these solutions in more detail.
4.1. Choose a VPN server closer to your physical location
This is often the single most effective way to boost your VPN speed. As we discussed, how far data has to travel directly impacts overall speed. Most VPN applications provide a list of server locations you can choose from.
Your best bet is to prioritize servers in your own country or nearby countries. For example, if you’re located in California, try connecting to servers on the US West Coast first (like Los Angeles, San Francisco, or Seattle). If you need an IP from another country, choose a server in a major city. For example, a London server offers better connectivity than an obscure location. The shorter the journey for your data, the quicker your connection will likely be.
4.2. Select a less crowded server (check server load if available)
Just like a physical highway, a VPN server can get congested if too many people are using it at once. A server with fewer users generally means more resources and better speeds for you.
Some VPN providers helpfully display the current load on their servers, often as a percentage (e.g., “75% load”) or with a color code. If this information is available, opt for servers with a lower load percentage.
If your VPN app doesn’t show server load, don’t be afraid to manually switch between a few different servers in your target region. You might find one that’s significantly less congested and therefore faster.
4.3. Experiment with different VPN protocols
As we covered earlier, the method you use can make a difference. Most VPN apps default to a specific protocol, but many allow you to change it in the settings.
Here’s a general order you might want to try, if available:
- WireGuard: Often the fastest and most modern option.
- IKEv2/IPSec: Known for speed and stability, especially on mobile.
- OpenVPN (UDP): Generally faster than its TCP counterpart.
- OpenVPN (TCP): Typically the slowest, but the most reliable for getting through restrictive networks.
I’ve often found in my tests at Safelyo that switching to WireGuard, where available, provides an immediate and noticeable speed improvement. It only takes a few seconds to change protocols, so it’s well worth experimenting.
4.4. Use a wired Ethernet connection instead of Wi-Fi
While a wireless connection like Wi-Fi is convenient, it’s more prone to interference than a stable wired connection. If your device supports it, plugging directly into your router with an Ethernet cable can provide a more stable and potentially faster internet connection overall.
This stability can, in turn, help your VPN perform better. This is particularly beneficial for bandwidth-intensive activities like online gaming, where low latency is critical, or when streaming 4K video content, where a consistent, fast connection prevents buffering.
4.5. Restart your modem, router, and device(s)
Ah, the classic “perform a reboot” advice. It might sound too simple, but restarting your devices can often resolve temporary glitches in your network setup.
Give them all a fresh start – sometimes, that’s all it takes to see an improvement. It’s a quick and easy troubleshooting step that costs nothing but a few minutes.
4.6. Temporarily disable interfering software
Sometimes, other security software on your computer, like your firewall or antivirus program, can conflict with your VPN connection or inspect its traffic, which can cause slowdowns.
As a temporary troubleshooting step, you can try disabling these programs one by one to see if your VPN speed improves. Crucially, this is for testing purposes only.
If you find that disabling a particular piece of software does speed up your VPN, do not leave it disabled permanently. Instead, look for an option within that software to add your VPN application to an “exceptions” or “whitelist”. This allows the VPN to operate without interference while keeping your system protected.
4.7. Consider upgrading your internet plan if your baseline is slow
This goes back to the point that a VPN can’t make your internet faster than what your ISP provides. If your basic internet connection is very slow, VPN optimizations may not be enough. You might still not have a smooth online experience.
If you’ve tried all other troubleshooting steps and your VPN speed is still unacceptably slow relative to your baseline, and that baseline itself is low, it might be time to consider upgrading your internet package from your ISP. A faster foundational speed will give your VPN more bandwidth to work with.
4.8. Avoid unreliable free VPNs
It can be tempting to opt for a free VPN service, but when it comes to speed (and often security), you generally get what you pay for. Free VPNs are notorious for slow speeds due to several reasons:
- Fewer servers: Leading to overcrowding.
- Overloaded servers: Too many users sharing limited resources.
- Bandwidth throttling: Deliberately limiting your speed.
- Outdated infrastructure: Not investing in fast servers or protocols.
- Sometimes, they might even sell your browsing data to cover costs, which defeats the primary purpose of using a VPN.
In my experience helping remote teams set up secure VPN connections, I’ve seen this issue firsthand. One user relied on a free VPN while working abroad and kept running into painfully slow upload speeds. After switching to a reputable paid provider with stable servers and no throttling, the issue disappeared. It was a clear reminder: While free sounds appealing, the poor user experience often comes with frustration and wasted time.
My advice? Investing in a reputable paid VPN service is almost always a better long-term choice for both speed and reliable security. Many offer money-back guarantees, so you can test them out risk-free. Using a free VPN slow internet experience is a common complaint for a reason.
4.9. Utilize split tunneling (if available)
Split tunneling is a handy feature offered by many modern VPNs. It allows you to choose which apps or websites use the VPN connection and which ones connect directly to the internet without going through the VPN.
How does this help speed? Some apps don’t require VPN protection, like local banking or online games. You can exclude these applications from the VPN tunnel for better performance. This frees up VPN bandwidth and can improve the speed of those specific apps.
For instance, use the VPN for your torrent client for added confidentiality But allow Netflix to connect directly when watching local content for the best quality.
Check your VPN’s settings to see if it offers this feature (sometimes called “whitelisting” or “selective routing”). It can be a great way to balance security needs with performance. Note that some advanced users use VPN bonding to combine multiple connections, but this is a different technology.
5. Can a VPN increase your internet speed?
Now, this might sound counterintuitive, but yes, in a few specific scenarios, a service could actually make your connection feel faster.
It’s important to understand that these are exceptions rather than the rule, and a VPN’s primary job is security, not speed boosting. However, it’s worth knowing when you might get this unexpected perk.
So, can a VPN increase internet speed? Let’s explore.
5.1. Bypassing ISP throttling
Throttling is when your Internet Service Provider (ISP) deliberately slows down certain types of internet traffic or your entire connection after you’ve used a certain amount of data. They might do this for activities like peer-to-peer (P2P) file sharing (torrents), streaming high-definition video, or online gaming, especially during peak hours, to manage network congestion.
One of the most common instances where a service might “speed up” your connection is by helping you bypass intentional slowdowns from your provider. How does a VPN help? By encrypting your internet traffic, a VPN hides the type of data you’re sending and receiving from your ISP. If your ISP can’t see what you’re doing online, it can’t selectively throttle specific activities.
If your ISP slows down Netflix or torrents, a VPN can make them faster. It bypasses the artificial speed limits that your internet provider imposes.
5.2. Improving routing paths
Sometimes, the default path your ISP uses to route your internet traffic to a particular website or online service isn’t the most efficient one. Your data might be taking a longer, more congested route than necessary.
In some cases, connecting to a VPN server can inadvertently place you on a more direct or less congested network path to your final destination. The VPN server might have better peering arrangements or simply be located on a “faster lane” of the internet backbone for that specific connection.
This scenario is less common than bypassing throttling, but it can happen, particularly for international connections where routing can be complex. You might find that accessing a server in another country is quicker via a strategically located VPN server than through your ISP’s default route.
It’s important to reiterate: these are exceptional circumstances. You shouldn’t subscribe to a VPN expecting it to turbocharge your general internet speeds. However, if you’re experiencing ISP throttling or suboptimal routing for specific services, a VPN could offer a surprising improvement.
6. Choosing a VPN that prioritizes speed without compromising security
If consistently fast performance is high on your priority list (and for most of us, it is), then choosing the right VPN provider is absolutely crucial. Not all VPN services are created equal, especially when it comes to the engineering and infrastructure that support fast connection speeds while maintaining robust security.
So, what should you look for in a VPN if speed is a major concern? Here are the key factors:
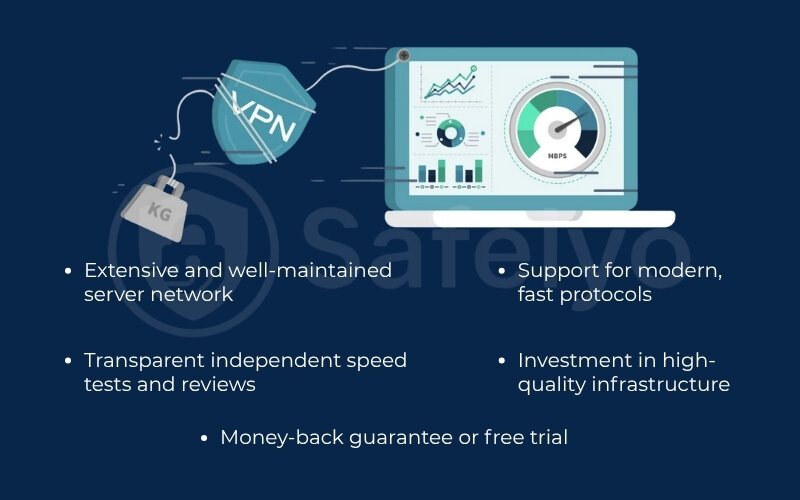
Extensive and well-maintained server network
A provider with a large number of servers in diverse locations gives you more options to find one that’s close to you and not overcrowded. Look for providers who regularly update and optimize their server infrastructure.
Support for modern, fast protocols
As we’ve discussed, protocols like WireGuard are a game-changer for speed. Prioritize providers that offer WireGuard or have their own proprietary technologies engineered for high throughput.
Investment in high-quality infrastructure
Top-tier VPNs invest in servers with high-bandwidth ports (e.g., 10 Gbps or even higher) and have excellent peering relationships with internet backbones. This backend capability is vital for handling large volumes of traffic without slowing down.
Transparent independent speed tests and reviews
Look for reviews and tests from reputable third-party sources. Here at Safelyo, we conduct our own in-depth VPN reviews, including specific speed tests that show the percentage of speed drop and compare internet speed with VPN vs without, to give you a clear picture. Seek out reviews that provide actual data, not just vague claims.
Money-back guarantee or free trial
The best way to know if a VPN is fast for you is to test it yourself. A generous money-back guarantee (typically 30 days) or a limited free trial allows you to run your own speed tests on your usual connections and servers before committing long-term.
My advice is simple: Don’t just look at the price tag. A slightly more expensive VPN from a reputable provider often translates to a significantly better experience in terms of speed, reliability, and security. It’s an investment in a smoother, safer online experience.
>> For more guidance, consider checking out our detailed Best VPN reviews on Safelyo. We break down the performance, security features, and usability of leading VPN services to help you find the best fit for your needs.
7. FAQ about VPN speed issues
Here are answers to some common questions people have when they experience or worry about VPNs affecting their internet speed. Understanding these VPN speed issues can help you troubleshoot and set realistic expectations.
How much internet speed loss is considered normal with a VPN?
A 10-30% speed decrease is typical with a quality VPN. This can vary based on server distance, protocol, server load, and your base internet speed.
What are the main causes of VPN slowdowns?
Key causes include encryption processing, server distance, overcrowding, server quality, and the protocol selected. Your own internet speed also sets the upper limit.
What is considered a good VPN speed?
A good VPN speed retains 70-90% of your original internet speed and remains sufficient for your online activities (e.g., smooth HD streaming, low-ping gaming). It’s relative to your baseline and needs.
What are the other possible drawbacks of using a VPN?
Other potential downsides can include subscription costs, some sites blocking VPN IPs, and occasional extra CAPTCHAs. However, security and privacy benefits usually outweigh these.
Should I keep my VPN on all the time?
Yes, for maximum security and privacy, especially on public Wi-Fi or when handling sensitive data. You can selectively turn it off for non-critical, speed-sensitive tasks or use split tunneling if available.
8. Conclusion
So, to wrap things up, the answer to the burning question, “Does VPN slow down internet?” is generally yes, it can. But as we’ve explored, the extent of this slowdown isn’t set in stone, and more importantly, it’s often something you can actively manage and minimize.
Let’s quickly recap the key takeaways to remember:
- Why it happens: VPNs can slow your connection due to essential processes like data encryption, the physical distance to servers, server load, and the protocol in use.
- You can fight back: There are many effective ways to boost your VPN speed. Try choosing closer servers, experimenting with protocols, or using a wired internet connection.
- Testing is key: Regularly testing your speed with and without the VPN helps you understand its impact and the effectiveness of your optimization efforts.
- Choose wisely: Selecting a high-quality provider that invests in robust infrastructure is fundamental for a fast and safe experience.
- Rare speed boosts: In some specific situations, like bypassing ISP throttling, a VPN might even give your internet a little pick-me-up.
For more in-depth guides, expert VPN reviews focusing on speed and security, and other valuable tech insights, continue exploring the Privacy & Security Basics category here on Safelyo. We’re here to arm you with the knowledge you need to master your digital world!