Are you confused about the difference between a Proxy vs VPN? While both tools hide your IP address and help you access restricted content, they operate very differently. A proxy works like a simple mask for your location, whereas a VPN acts as a secure, encrypted tunnel for your entire digital life.
This guide breaks down the critical differences to help you decide which tool fits your needs. You will compare their speed, security levels, and use cases to ensure you are not leaving your personal data exposed.
Key takeaways:
- The main difference: A VPN encrypts your data for safety; a proxy does not.
- Scope: VPNs secure your entire device, while proxies usually only cover a single app.
- Privacy: Only a VPN hides your activity from your ISP and protects you on public Wi-Fi.
- Performance: Proxies are often faster for streaming, but VPNs offer better reliability.
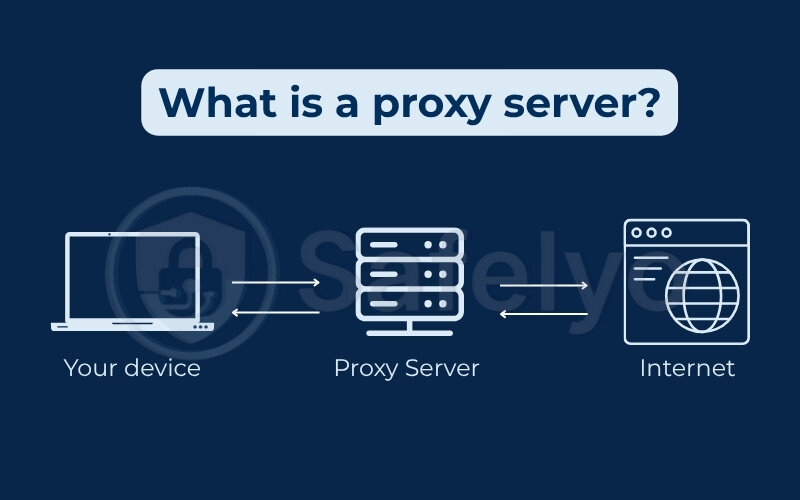
1. What is a proxy server?
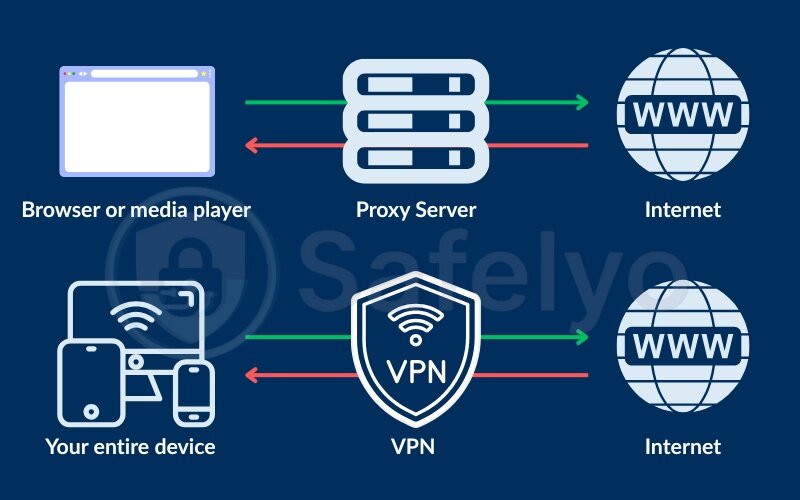
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your device and the internet. When you use a proxy, your internet traffic is routed through this server, which changes your visible IP address before reaching the final website or service. This can help you mask your location, bypass basic geo-blocks, or access filtered content.
- How proxies work:
- You connect to the proxy server instead of going straight to the website.
- The proxy forwards your request, receives data, and returns it to you, often with your IP address hidden from the site you’re visiting.
- Popular proxy types:
- HTTP proxies: Good for browsing websites.
- SOCKS proxies: Versatile, supporting more types of traffic (like video or games).
- Transparent proxies: Sometimes used by businesses to filter or monitor network usage.
Proxies are easy to set up, often through your browser or a small app, making them a favorite for users wanting a simple privacy boost without much complexity.
Next, we’ll look at what a VPN is and how it differs from a proxy server.
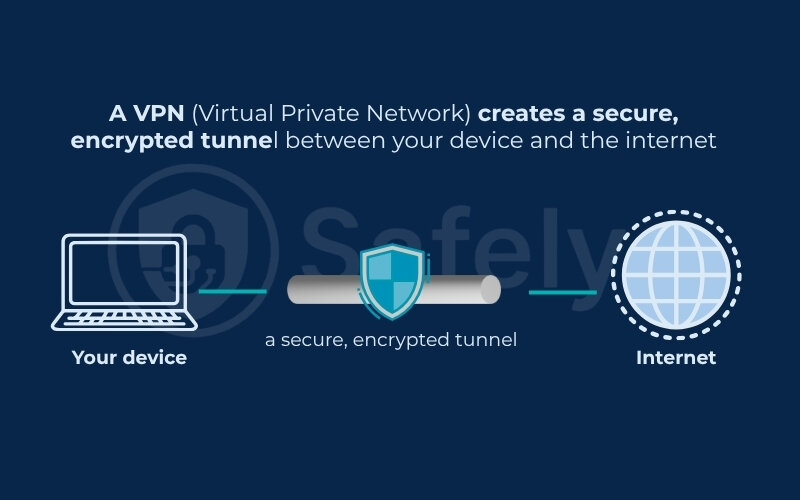
2. What is a VPN?
Understanding “what is a VPN“ helps clarify how it differs from a proxy server, especially regarding privacy, encryption, and online protection.
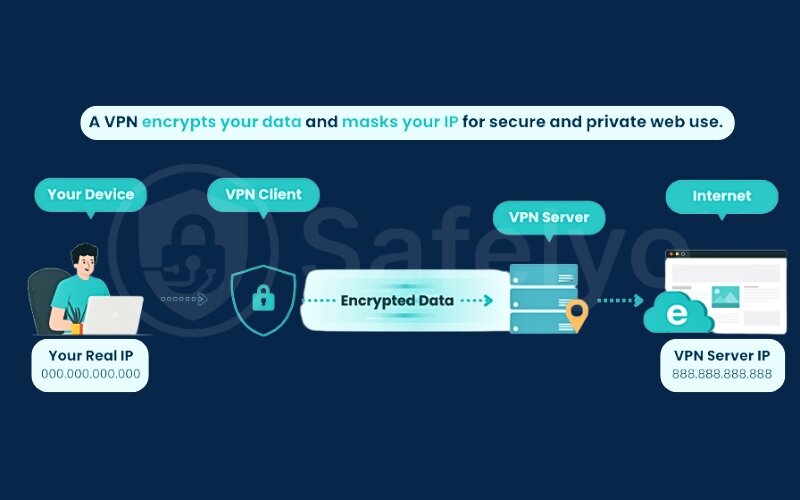
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a security tool that creates an encrypted tunnel between your device and the internet. When you connect to a VPN, your entire online activity – from browsers to apps – is securely routed through a remote VPN server. This not only hides your IP address (like a proxy) but also encrypts your data, making it unreadable to hackers, ISPs, or anyone else trying to snoop on your activity.

- How VPNs work:
- Your device encrypts all outgoing data before sending it to the VPN server.
- The VPN server forwards your requests to websites and services.
- Encrypted responses return to your device, keeping your actions and personal data private.

- Typical features of VPNs:
- Device-wide protection covering all internet traffic
- Strong encryption standards (such as AES-256-bit)
- Masking your real IP address, no matter which app or browser you use
- Secure browsing, especially on public Wi-Fi or when accessing sensitive data
VPNs are trusted by individuals and professionals alike. As the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) describes, “VPNs offer a greater level of privacy and security than most proxies because they use secure tunneling and encryption to ensure data confidentiality.”
Read more:
Next, I’ll directly compare proxy vs VPN: key differences in privacy, speed, security, and use cases.
3. Proxy vs VPN: Key differences
Choosing between a proxy and a VPN depends on several key differences. Including how they handle your data, what level of protection they offer, and how they affect your browsing experience.
In this section, I break down the technical and practical distinctions to help you make an informed choice.
3.1. Encryption and data safety
The main distinction between a proxy and a VPN lies in how they secure your data. While both help mask your IP address, only one offers real encryption:
- VPNs encrypt your entire internet connection, creating a secure tunnel between your device and the web. Protecting activities like banking, emailing, and messaging even on public Wi-Fi.
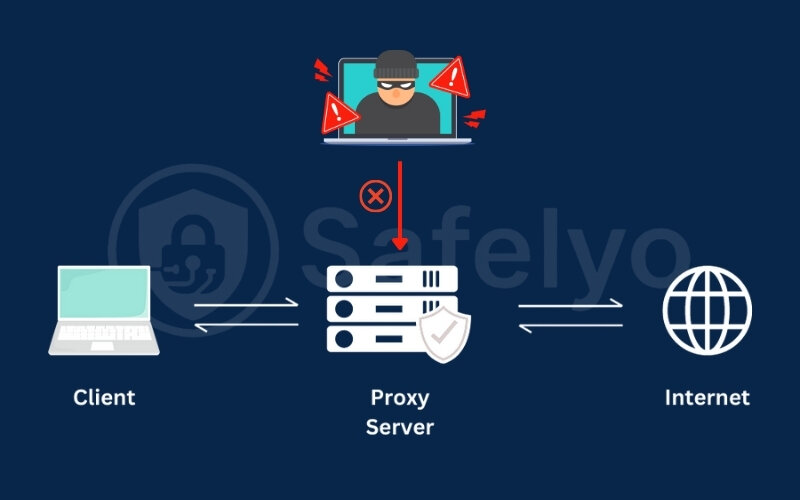
- Proxies do not provide encryption, meaning your internet traffic can still be seen by your ISP, network administrators, or attackers on shared networks.
When I traveled to a conference and had to send contracts from an airport lounge, I relied on a VPN to ensure full encryption. A proxy wouldn’t have protected those files from potential snooping on the shared network.
According to Norton, “VPNs offer robust encryption, making them ideal for anyone needing security on unsecured networks.”
3.2. Scope: app vs device-wide protection
Another key difference lies in how broadly each tool protects your traffic. This can dramatically affect your online security without you realizing it.
- VPNs protect your entire device, routing all traffic web browsers, apps, and background services through an encrypted connection.
- Proxies only protect the application they’re configured in, such as a browser or media player. Other apps bypass the proxy unless set up separately.
In a recent project, I set up a proxy just for my browser to access some regional websites. It worked seamlessly for that purpose. However, if I had needed to secure my email or messaging apps as well, a VPN would have been necessary.
3.3. Privacy, anonymity, and ISP visibility
If your main concern is staying anonymous or keeping your activity private from your ISP, the comparison between proxy server vs VPN becomes even more important.
- VPNs hide both your IP address and your browsing activity from your ISP and external trackers. Thanks to tunneling and encryption.
- Proxies only hide your IP, so your ISP can still see your destinations, and your browsing sessions remain unsecured.
- VPNs also rotate IPs or use shared IPs, adding another layer of anonymity in multi-user pools.
One of my clients wanted to prevent targeted ads from tracking company research trends. Moving their team off a proxy to a VPN not only hid their activity from their ISP but also stopped behavior-based ad tracking.
As noted by CISA, “VPNs help reduce the risk of traffic interception by encrypting all transmissions, compared to most proxies, which lack this feature.”
3.4. Speed and performance (encryption’s impact)
Speed often factors heavily into the vpn vs proxy decision. Here’s how each tool affects performance:
- Proxies tend to be faster, especially free or simple ones, because they don’t encrypt traffic. This makes them suitable for quick browsing or accessing region-locked websites.
- VPNs may reduce speed slightly, due to the encryption process. However, premium VPNs often use high-speed servers and split tunneling to reduce slowdown.
There was a time when I needed to stream live foreign sports channels. A VPN caused a slight lag, so I switched to a proxy for this particular task. The stream ran smoothly and the broadcast quality was great, proving that for some speed-sensitive tasks, proxies can really shine.
3.5. Cost and common pricing models
Lastly, cost is a real differentiator for many users. Both options have free and paid versions, but the benefits vary considerably:
- Proxies are usually free or very cheap. Some premium proxy providers charge per GB or offer monthly rates for anonymity-based use cases like scraping or automation.
- VPNs typically charge a monthly or annual subscription, often including secure servers, no-logs policies, malware blockers, and multi-device support.
I initially tried a free proxy for streaming, but frequent disconnects and intrusive ads made it unreliable. Paying for a VPN removed the interruptions and gave me consistent access to geo-restricted content and strong privacy assurances.
4. When to use a proxy vs VPN
Many users wonder whether a proxy or VPN is better for their daily needs or if they even need both. To make this choice easier, let’s look at real-life scenarios, typical use cases, and crucial risks for each tool.
A friend of mine once needed fast access to a streaming service only available abroad. The goal was simply to watch content, not to secure personal data. For this purpose, a proxy worked perfectly: setup was quick, speeds were great, and there was no noticeable lag. But there were also times, like connecting to public Wi-Fi at a hotel, when using a VPN was essential for protecting sensitive work emails and personal accounts against possible hackers.
Here are the most common use cases and warnings for both options:
4.1. Best situations to use a proxy
You might prefer a proxy when your need is simple IP masking or content access with minimal effort. Proxies are lightweight, straightforward, and often faster for basic activities.
Use a proxy for:
- Bypassing geo-blocks: Accessing region-locked websites or streaming content.
- Light browsing: Hiding your IP for basic, non-sensitive activities.
- Web scraping or automation: Running tasks that require changing IPs quickly without full-device security.
- Improving speed or reducing bandwidth load: Some organizations use proxies for caching and load balancing.


4.2. Best situations to use a VPN
A VPN is your go-to choice for privacy, data security, and device-wide protection.
VPNs are invaluable when:
- Handling sensitive information: Using online banking, sending confidential work files, or transmitting private data.
- Connecting to public Wi-Fi: Encrypting all your internet traffic in hotels, airports, or cafés, protecting you from cyber threats.
- Avoiding ISP surveillance: Hiding browsing activity from your internet service provider.
- Secure remote work: Safeguarding company data when working from home or abroad.
- Bypassing censorship or strict regional controls: Accessing blocked or restricted services securely.
See also:
4.3. Risks: What not to use each for
Each tool has its limitations—and using the wrong one carries real risks.
Avoid using proxies for:
- Transmitting passwords, payment info, or any personal data: proxies don’t encrypt your traffic, exposing you to hackers or data leaks.
- Long-term business use without due diligence: Many free or poorly managed proxies log your activity or inject ads and malware.
Avoid using VPNs for:
- Circumventing service restrictions where VPN use may violate terms: this could result in account bans or connection issues.
- Relying solely on VPNs for all security: misconfigured VPNs can leak data, and not all VPN providers are equally trustworthy. Always choose services with strong privacy policies and a good security reputation.
Ready to compare proxies and VPNs side by side? The next section includes a quick comparison table for fast decision-making.
5. Quick comparison table: Proxy vs VPN
To help you compare at a glance, here’s a side-by-side summary of the main features, strengths, and limitations of a proxy vs VPN.
This table gives you a quick way to spot which solution best matches your privacy and usage needs.
| Feature | Proxy | VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | No encryption; data is visible to others | Encrypts all traffic between device and server |
| Scope of protection | Application-specific (browser, streaming app) | Device-wide: all apps and services covered |
| IP masking | Yes | Yes |
| ISP visibility | ISP can see visited sites and data | ISP cannot see sites or data |
| Speed | Usually faster (no encryption overhead) | May be slightly slower (encryption used) |
| Privacy & anonymity | Basic; IP only | High; IP and activity hidden |
| Best use cases | Bypassing geo-blocks, light browsing, scraping | Sensitive tasks, public Wi-Fi, full privacy |
| Cost | Free or low-cost options available | Usually requires subscription |
| Common limitations | No data security, risk of logging/ads/injection | May slow speed, requires trusted provider |
Use this table to quickly match your online activities and level of privacy concern with the most suitable tool.
Ready for help on how to decide which option fits your situation? If so, let’s move to the next section!
6. How to decide: Proxy or VPN?
Still unsure whether to go with a proxy or a VPN? Let’s break it down with a few simple questions that point you toward the right tool based on what really matters: your activity, your security needs, and your browsing habits.
6.1. Ask yourself these quick questions
Use these questions to narrow down your choice in seconds:
- Do you need encryption for sensitive transactions or data?
→ Choose a VPN. Proxies don’t offer encryption. - Are you just trying to access geo-blocked websites or content?
→ A proxy is usually sufficient for casual tasks like this. - Do you use public Wi-Fi often (hotels, cafés, co-working spaces)?
→ Go with a VPN to protect your data from potential snoopers on open networks. - Are you trying to secure all apps on your device, not just a browser?
→ VPNs offer whole-device protection. Proxies cover apps individually.
6.2. Recommendations by user type
Here’s how the decision might look based on your typical internet use case:
| User Type | Recommended Option | Why |
|---|---|---|
| Casual user | Proxy | For basic IP masking and faster browsing |
| Streamer | Proxy or VPN | Proxy works for region-access; VPN adds privacy |
| Remote worker | VPN | Encrypts data, protects work apps, defends on public Wi-Fi |
| Online shopper | VPN | Secures personal info and payment details |
| Privacy advocate | VPN | Hides activity from ISP and third-party trackers |
When providing tech guidance to a freelance writer last year, I learned they just needed to view region-specific articles. A lightweight proxy was enough. But when they later began sending client contracts from coffee shops, we switched to a VPN, it matched their increased security needs without complicating daily tasks.
7. FAQs on VPN vs Proxy
Got lingering questions about the choice between proxy vs VPN? Here are the most common ones explained in plain language, so you can feel confident moving forward.
Is a free proxy safe?
Free proxies can be risky. While they allow you to change your IP address or access blocked content, many free providers log your activity, inject ads, or introduce malware. They also don’t encrypt your traffic, which makes sensitive online actions unsafe.
If you use a free proxy, avoid logging into accounts, submitting personal data, or sending payment info.
Can I use both a proxy and a VPN?
Yes, but it’s rarely necessary. In some advanced setups, users route traffic through a proxy after the VPN tunnel for added IP masking, but this requires careful configuration and trust in both services.
For most users, using a reliable VPN alone is more secure and efficient than combining both.
Will a VPN slow down my internet?
It might, but not by much if you’re using a quality provider. Since a VPN encrypts your traffic and routes it through a secure server, some speed loss can happenm especially if you choose a server far from your location.
That said, many top VPNs now offer high-speed servers and protocols (like WireGuard®), which keep performance and lag issues minimal.
Read more: Does VPN slow down internet? YES, but here’s why & 10 ways to fix it!
Do proxies hide my activity from my ISP?
No, proxies do not hide your online activity from your ISP. They can mask your IP address from websites you visit, but your ISP can still see what websites you’re accessing and how much data you’re using.
Only a VPN with encryption can prevent your ISP from viewing your internet activity.
8. Conclusion
Choosing between a proxy and a VPN ultimately comes down to what you value most: convenience, privacy, speed, or security. In the ongoing proxy vs VPN debate, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution, but understanding their core differences helps you make a smarter choice.
Key takeaways:
- VPNs provide end-to-end encryption and full-device protection, ideal for handling sensitive data or using public Wi-Fi.
- Proxies are better for lightweight tasks, like bypassing geo-restrictions or performing anonymous, low-risk browsing.
- VPNs protect all apps on your device, while proxies only work in specific applications unless manually configured.
- Proxies are often free or lower-cost, but may carry risks like tracking or data leakage.
- Avoid using proxies for confidential activities, as they don’t encrypt your traffic.
When I first started working remotely, I used a proxy to access regional dashboards during travel. It was quick and efficient. But as my work involved more contracts, logins, and sensitive communication, I switched to a VPN. It took slightly longer to set up—but the peace of mind it offered on public Wi-Fi was more than worth it.
Think through your needs before you choose, and you’ll get the right balance between convenience and security.
For more straightforward tech guides like this, check out the “Privacy & Security Basics” section at Safelyo. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to level up your digital privacy, we’ve got more resources to support you.