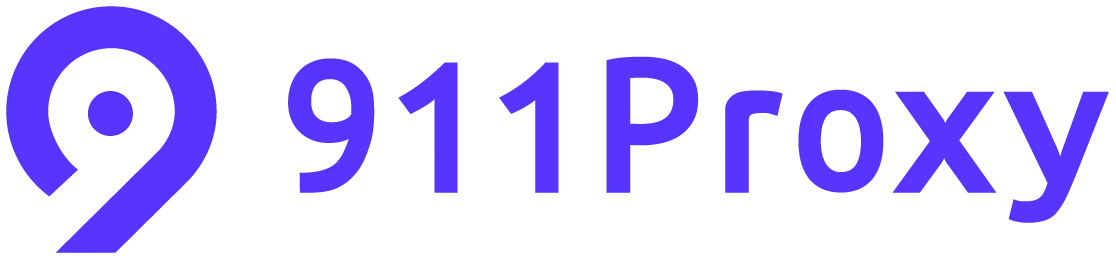In today’s increasingly complex digital world, understanding how to safeguard your information and bolster your online security isn’t just an advantage – it’s essential. Whether you’re working remotely, managing finances online, or simply browsing on public Wi-Fi, a VPN tunnel provides that crucial layer of protection, giving you greater peace of mind.
Ever wondered what is a VPN tunnel and why it’s such a buzzword when we talk about online safety? Imagine it as your very own secret, encrypted pipeline for your data. This digital passage helps shield your personal information from prying eyes and cleverly masks your real IP address whenever you surf the web.
Drawing from my practical experience in cybersecurity, I’ve seen firsthand how users can become targets for data breaches simply by overlooking this straightforward yet powerful tool.
In this simple guide, you’ll discover:
- What a VPN tunnel actually is, explained in plain language.
- The key benefits of using one for your online activities.
- A step-by-step breakdown of how VPN tunneling works to protect you.
- Distinguishing between a VPN tunnel, the overall service.
Let’s explore together exactly how a VPN tunnel functions and why it should be your first line of defense in the digital realm.
1. What is a VPN tunnel?
At its heart, a VPN tunnel is essentially a private, secure, and encrypted connection created between your device (like your computer or smartphone) and the internet. Think of it as a shielded passageway that your online data travels through, keeping it hidden and protected from anyone who might be trying to peek. This connection is established via a dedicated VPN server.
To make this VPN tunneling explained concept even clearer, let’s use an example. Imagine you need to send a highly confidential message.
- Sending data without a VPN is like mailing a postcard: Anyone who handles it can read the message.
- Now, with a VPN, you first write your message (your data).
- Then, you place it into a special, opaque envelope (this is called encapsulation).
- Next, this envelope is placed inside a super-strong, locked metal box (this represents encryption, making the contents unreadable).
- Finally, this locked box is sent directly to the recipient via a private courier. This secure route is your VPN tunnel, bypassing the public postal system where it could be intercepted.
The primary purpose of a VPN tunnel, therefore, is to create a confidential and secure communication channel for your internet traffic. It ensures that your data isn’t just floating out in the open, vulnerable to snoopers, hackers, or even your internet service provider (ISP), who might be tracking your online activities.
>> You might also like these related articles:
2. Why should you care about a VPN tunnel?
So, you understand what a VPN tunnel is, but why is it so important for your daily internet use?
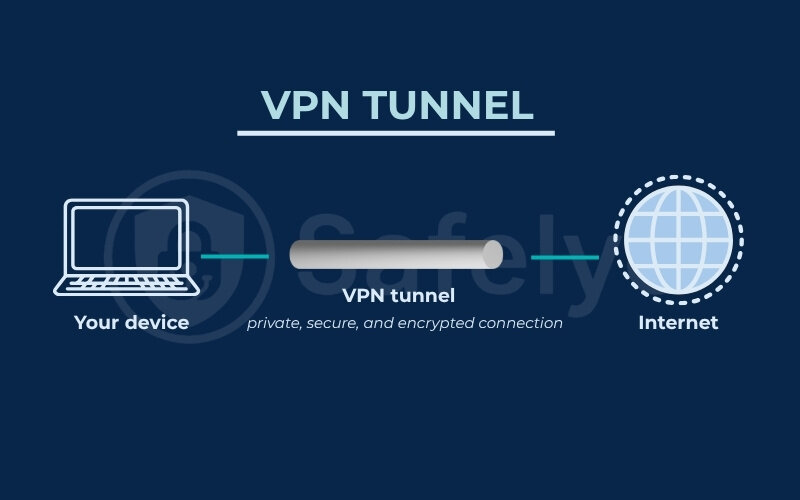
Well, the VPN tunnel benefits are quite significant, essentially transforming how you interact with the online world. It acts as a powerful shield, and understanding what does a VPN tunnel do in practical terms can make a real difference to your digital life. Let’s break down the key advantages of using a VPN tunnel.
2.1. Enhanced online security
On free Wi-Fi networks, your data is vulnerable. It is exposed to threats like packet sniffing by hackers. A VPN tunnel encrypts your connection, making it incredibly difficult for hackers to intercept your sensitive information, such as login credentials or credit card details. This encryption also helps protect you from “man-in-the-middle” attacks, where an attacker secretly relays and possibly alters the communication between two parties.
2.2. Keeping your activities private
Your internet service provider (ISP) can see every website you visit, how long you stay there, and what you do. This information can be logged, sold to advertisers, or even handed over to authorities.
A VPN tunnel shields your online activities from your ISP by routing your traffic through its encrypted pathway. This means your browsing history, downloads, and other online actions remain private, giving you control over who sees your digital footprint. It’s about keeping your personal business, personal.
>> You may also be interested in: Can my ISP see my browsing history? And how to become invisible
2.3. Hiding your digital footprint
Every internet-connected device has a unique IP address, similar to a digital home address, used for tracking. When you use this secure pathway, your actual IP address VPN is masked and substituted with the address of the server you are using.
This makes it harder for websites and advertisers to trace your online activities. As a result, you can browse the web with a greater degree of obscurity.
2.4. Accessing content freely
While the core strengths of a VPN tunnel lie in security and privacy, a common side benefit is the ability to access a wider range of online content.
By connecting to a VPN server in a different country, you can sometimes bypass geo-restrictions placed on websites, streaming services, or online games. It’s important to remember this is a consequence of how VPNs route traffic, not always its primary design focus for every user.
>> Read more: What is geoblocking? Meaning, examples & How to bypass
3. Key components involved in VPN tunneling
To truly grasp how a VPN tunnel works its magic, it’s helpful to understand the main “actors” involved in creating and maintaining this secure connection. These are the fundamental building blocks that work together seamlessly behind the scenes. These components are the backbone of your online protection.
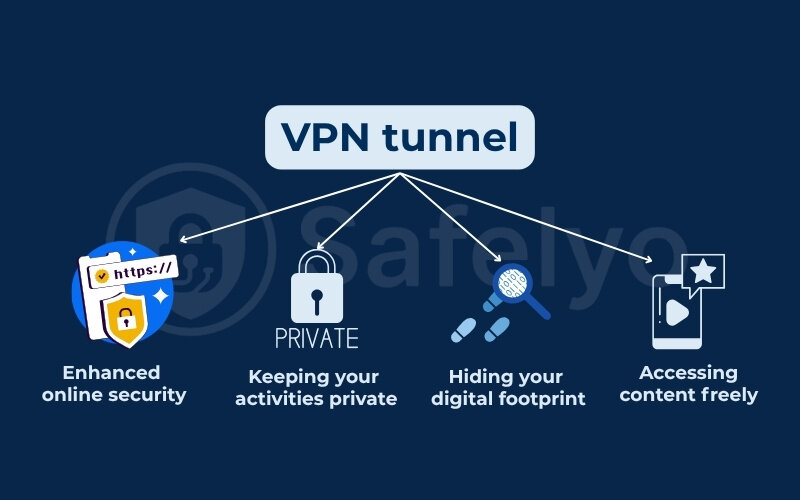
VPN Client
The VPN client is your gateway to the VPN service. This is the software or application you install on your device – whether it’s your computer, smartphone, or tablet.
It’s responsible for initiating the connection to a VPN server and handling the encryption and decryption processes on your end. Think of it as the local command center for your VPN activities.
VPN Server
This is a powerful, specially configured remote computer owned and operated by the VPN provider. When you activate your VPN, your client connects to one of these servers.
The VPN server acts as a secure intermediary between your device and the wider internet. It receives your encrypted data, decrypts it, and then forwards your request to the intended website or online service using its own IP address.
VPN Protocols
These are the sets of rules and instructions that determine how the VPN tunnel is actually built and how your data is packaged and secured. VPN protocols define the encryption standards and transmission methods used for the tunnel. There are various protocols available, each with different strengths.
From my experience reviewing numerous VPN services, I can’t stress enough how crucial it is to choose a reputable VPN provider. A provider with a well-designed client, a stable and geographically diverse server network, and support for strong, modern VPN protocols is paramount for a reliable and secure VPN tunneling experience.
4. The step-by-step process of how a VPN tunnel works
Now that we know the “what” and “why,” let’s explore the “how.” Understanding how a VPN tunnel works involves a fascinating sequence of events that ensures your data remains secure and private.
While it might sound technical, the actual process of how tunneling is accomplished in a VPN can be broken down into a few key stages. This is where your data gets its special treatment, creating that encrypted VPN tunnel.
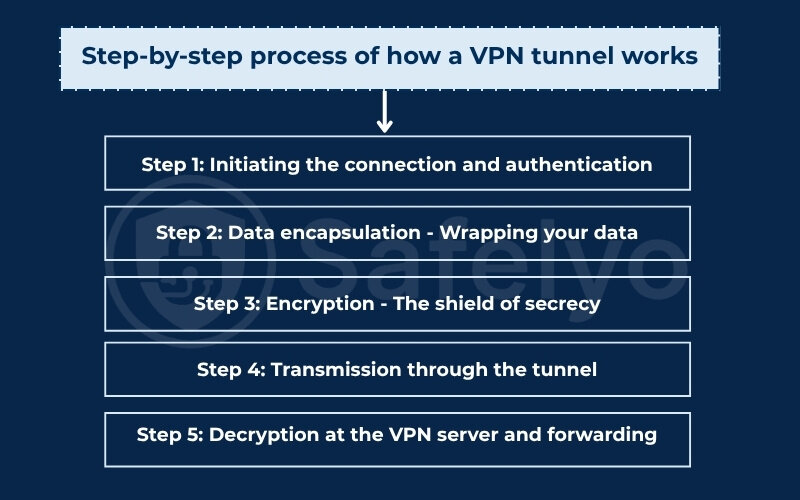
4.1. Step 1: Initiating the connection and authentication
The process begins when you launch the client application on your device and select a server (the app on your device, like VPN on iPhone or VPN on Android). Your device then sends an initial connection request to that location.
Your client and the server ‘shake hands’. They use a method like Diffie-Hellman key exchange to securely agree on decryption key. This is the authentication phase. It ensures that you’re connecting to a legitimate VPN server, and the server confirms that you are an authorized user.
4.2. Step 2: Data encapsulation – Wrapping your data
Once authentication is successful, the process of data encapsulation begins. It’s like giving your message a special wrapper before it’s made unreadable.
Think of data encapsulation as putting your original internet message (like the web address you want to visit) inside a protective container. This container also includes instructions for how it should be handled by the VPN server, but it effectively hides your original data from the outside internet.
4.3. Step 3: Encryption – The shield of secrecy
This is where the core of VPN encryption happens, and it’s a critical part of the VPN tunnel security. The service then scrambles your data. It uses advanced cryptographic techniques and a complex mathematical algorithm. From my experience evaluating VPN security, top providers use incredibly strong “secret languages” like AES-256, which are virtually unbreakable with current technology.
Imagine the VPN rewriting your data in a special, secret language that only your device and the VPN server understand. Even if someone could intercept this data as it travels, it would look like complete gibberish to them.
4.4. Step 4: Transmission through the tunnel
With your data now encapsulated and heavily encrypted, it’s ready for its journey. The encrypted packet is sent from your device. This secure data transmission travels through the tunnel to the server.
This secure pathway is the VPN tunnel itself. Your ISP can see you’re sending encrypted data to a VPN server. However, they cannot see the data’s content or its final destination beyond that server.
4.5. Step 5: Decryption at the VPN server and forwarding
When the encrypted data packet arrives at the VPN server, the server uses its corresponding encryption key to unlock and unscramble the data, reverting it to its original form. The VPN server then removes the outer encapsulation layer.
Now, with your original request revealed, the VPN server forwards it to the intended website or online service using its own IP address, not yours. This effectively hides your true IP address and location from the destination site.
A website’s response is sent back to the VPN server, which encrypts it. The data is then sent through the tunnel to your device, where your VPN client decrypts it.
5. Is your VPN tunnel truly secure? Can it be hacked?
While a well-implemented VPN tunnel provides a formidable layer of protection, it’s important to have a realistic understanding. A common and very valid question is about the actual VPN tunnel security: Just how impenetrable is this digital fortress we’ve described?

No system is 100% immune to hacking. However, the effort required to breach a strong tunnel is immense. However, the likelihood of your VPN tunnel being compromised depends heavily on several critical factors. he tunnel’s security depends on several critical security measures:
The strength of the VPN protocol used
Modern protocols like OpenVPN and WireGuard are designed with robust security features. Older, outdated protocols (like PPTP) are known to have vulnerabilities and should generally be avoided if security is a top concern.
The robustness of the encryption algorithm:
As I mentioned earlier, strong encryption like AES-256-bit is the industry standard for reputable VPNs. Weaker encryption can be broken with sufficient computing power, although it remains a monumental task for strong algorithms.
Proper implementation and configuration
Even the best protocol and encryption can be undermined if the VPN provider hasn’t implemented them correctly or if there are misconfigurations in their server setup. This is where choosing a trustworthy and technically proficient VPN provider is vital.
Security of your own devices and the VPN server
The tunnel’s security can be undermined if your computer has malware or the VPN server is compromised. A server compromise is a rare event for top providers.
The "no-logs" policy of your VPN provider
Your data could be exposed if your VPN provider keeps activity logs. This can happen if their servers are compromised or they are legally forced to share data. A strict, audited no-logs policy is a cornerstone of a privacy-focused VPN.
From my experience analyzing various VPN services, I can confidently say that for the average internet user. A VPN tunnel from a reputable provider using modern protocols and strong encryption. It offers excellent security against common threats like ISP snooping, Wi-Fi hackers, and general online tracking. The effort and resources required to “hack” a properly secured VPN tunnel are immense, making individual users very unlikely targets for such sophisticated attacks.
The key takeaway is to choose your VPN provider wisely. Opt for services that are transparent about their security practices, use up-to-date protocols, and have a proven track record – these are the ones I consistently look for in my evaluations.
6. VPN tunnel vs. VPN vs. VPN server
When you start exploring the world of online privacy, you’ll often hear terms like VPN, VPN tunnel, and VPN server used. While they are all related, they refer to different aspects of the same protective technology. Understanding the distinction between the VPN tunnel vs VPN can help you grasp how it all works together.
So, is a VPN a tunnel? Not exactly, but a tunnel is a crucial part of a VPN. Let’s break them down:
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
The term ‘VPN’ refers to the overall technology that secures your connection on a public network. It includes all the software, hardware, and protocols that create this private link.
VPN Tunnel
This is the actual secure, encrypted connection that is established between your device and the VPN server. It’s the private pathway through which your internet data travels, shielded from outside eyes. The VPN tunnel is a core component and function of a VPN service.
VPN Server
This is a specific physical or virtual computer, owned and operated by the VPN provider, that your VPN client connects to. The VPN server authenticates your connection, decrypts your data, and sends it to the internet. It then receives, encrypts, and sends responses back to you through the tunnel. It acts as the gateway and a crucial intermediary.
To make it even clearer with an example: Imagine a private, high-speed railway system built just for you.
- Using an analogy, the service itself is like an entire railway company, including the trains, tracks, stations, staff, and schedules.
- The VPN server is like a specific train station. You go to this station to start your secure journey.
- The VPN tunnel is like a secure, protected railway track. It connects your device to the VPN server or connects two servers if data is being relayed. Your data travels safely on this exclusive track.
Here’s a quick comparison to highlight the differences:
| Feature | VPN | VPN Tunnel | VPN Server |
|---|---|---|---|
| What it is | The overall system/service for private networking | The secure, encrypted connection/pathway | The physical/virtual machine facilitates the connection |
| Analogy | The entire railway company | The protected railway track | A specific train station |
| Role | Provides the complete privacy solution | Transports data securely | Authenticates, encrypts/decrypts, and routes traffic |
| Tangibility | More of a concept/service | A functional pathway created by the VPN | A physical or virtual piece of hardware |
Understanding these distinctions helps you appreciate how each element contributes to your online security and privacy when you use a VPN service.
7. A brief overview of common VPN tunneling protocols
When we talk about how a VPN tunnel is created and maintained, we’re referring to the underlying VPN tunnel protocols. Think of these protocols as different “languages” or sets of rules that VPN clients and servers use to communicate securely.
There isn’t just one way to build a VPN tunnel – instead, there are various types of VPN tunnels defined by these protocols.
Many different VPN protocols exist for a reason. Each protocol is designed to balance different factors. These include performance, security, stability, and device compatibility. Some prioritize unbreakable encryption, while others focus on delivering the fastest possible connection speeds.
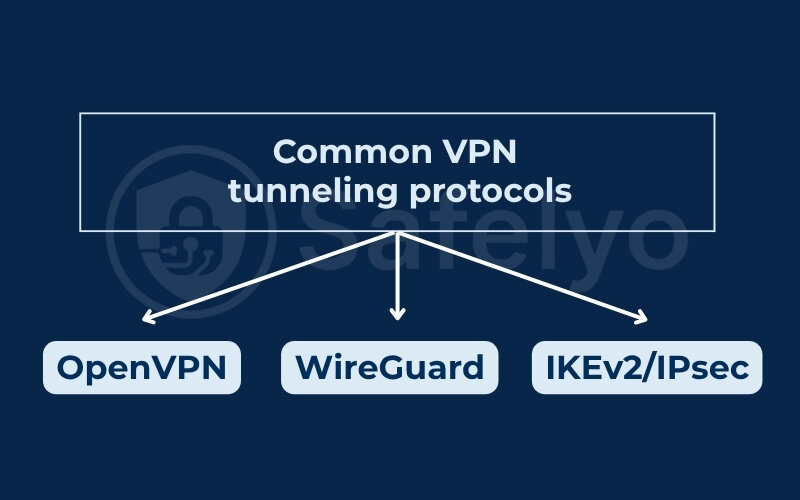
OpenVPN
This is a highly versatile and widely trusted protocol.
Known for its strong security and high configurability. It’s open-source, meaning its code is available for public scrutiny, which contributes to its reliability. It can run over either TCP (for reliability) or UDP (for speed) ports.
WireGuard
A relatively newer and increasingly popular protocol.
Praised for its exceptional speed and modern, streamlined codebase (much smaller than OpenVPN, making it easier to audit and potentially less prone to vulnerabilities). It aims to be faster and simpler without sacrificing security.
IKEv2/IPsec (Internet Key Exchange version 2 / Internet Protocol Security)
A robust and stable protocol.
Valued for its stability, especially on mobile devices, as it’s very good at automatically re-establishing a connection if it temporarily drops (like when switching between Wi-Fi and mobile data). It’s often fast and secure.
Many reputable VPN apps let you choose your protocol. They might also have an “automatic” setting that selects the best one for your network. Understanding these basic differences can help you make a more informed choice if you decide to experiment with these settings.
8. A quick look at VPN split tunneling: What you need to know
While a full VPN tunnel encrypts all your internet traffic, there’s a handy feature offered by many VPN services called Split Tunneling VPN. This feature gives you more flexibility over your internet traffic. You can decide which traffic uses the secure VPN and which accesses the internet directly.
Imagine you’re at home. With split tunneling, you can send your Chrome and email data through the encrypted VPN. This provides maximum privacy and security for those specific apps. For instance, I often use this when I’m researching sensitive topics for my Tech business or accessing my online banking – I want that traffic under the strongest protection.
Simultaneously, you might want to stream a local sports game that requires your regular IP address. You may also need to access a wireless printer on your home network. With split tunneling, you can exclude these specific apps or services from the VPN. So, your streaming app and your connection to the printer would bypass the VPN and connect directly.
Another commonly used case I’ve found useful is for online gaming. Some games are very sensitive to latency (ping). By using split tunneling, I can route my game traffic directly to the internet for the lowest possible ping, ensuring a smoother gaming experience, while all my other background applications (like cloud backups or general browsing) still benefit from the VPN’s security.
This feature is incredibly useful for balancing security needs with convenience or performance requirements. Of course, split-tunneling VPN is a more advanced feature. It’s like having two internet pathways from your computer at the same time: one super-secure, private lane (the VPN tunnel) for certain things, and another regular lane for other things that don’t need that level of protection or need direct local access.
8. FAQ about VPN tunnels
Here are answers to some common questions people have about VPN tunnels:
What does a VPN tunnel can do?
A VPN tunnel essentially creates a private and encrypted connection between your device and the internet. It protects your data from being intercepted by snoopers, hides your real IP address (enhancing your anonymity), and allows you to browse the web more securely and privately. Sometimes, it can also help you access content that might be geographically restricted. This is what a VPN tunnel does at its core.
How do I get a VPN tunnel?
The simplest way is to sign up for a reputable VPN service and download their application for your device (computer, smartphone, etc.). Once you connect to a VPN server through the app, the VPN tunnel is automatically established for you. There’s usually no complex manual configuration needed for everyday use.
What is the difference between a full tunnel and a VPN?
A Virtual Private Network is the technology that creates a private network over a public one. A “full tunnel” is a configuration where all of your device’s internet activity is routed through the encrypted connection. In contrast, “split tunneling” lets you route only some of your traffic through the secure pathway.
What is a VPN device tunnel?
A “VPN device tunnel” is an always-on VPN connection established by the device itself. For example, a computer connects as it starts up, even before a user logs in. This ensures all traffic from that device is consistently protected and is often used in business environments for secure remote device management.
How is tunneling accomplished in a VPN?
Tunneling in a VPN primarily involves two key processes working together. First is encapsulation, where your original data is wrapped inside other data packets, like putting a letter in an envelope. Second is encryption, where these encapsulated packets are scrambled into an unreadable code using a secret key, making them secure for transmission over the internet.
Are VPN tunnels always safe and unhackable?
When strong protocols (like OpenVPN or WireGuard) and robust encryption are used, VPN tunnels are very secure. However, no technology is 100% unhackable. The overall safety also depends on the VPN provider’s practices, correct configuration, and the general security of your own devices. For most users, a good VPN offers excellent protection.
Do I need to manually set up a VPN tunnel?
For most individual users, the answer is no. When you use a VPN application from a service provider, the app handles the entire VPN tunnel setup and management automatically. Manual setup is typically reserved for advanced users, specific business needs, or troubleshooting scenarios.
9. Conclusion
Understanding what is a VPN tunnel is truly the first step towards taking control of your online privacy and security in this digital age. It’s a fundamental concept that empowers you to navigate the internet with greater confidence.
To recap the main points we’ve covered:
- A VPN tunnel is essentially an encrypted, private connection that safeguards your data as it travels across the internet.
- It works its magic through processes like data encapsulation and strong encryption, creating a secure channel for your information.
- The key benefits include enhanced security (especially on free Wi-Fi), robust data privacy from ISPs and snoopers, and increased obscurity by masking your IP address.
- Choosing a VPN that uses modern protocols and a provider with a solid reputation for security is crucial for an effective and safe VPN tunnel.
While the underlying technology might seem a bit technical, using a VPN tunnel through today’s user-friendly VPN applications is remarkably simple and offers immense benefits. As I’ve seen in my work that it’s a foundational tool for anyone serious about their digital safety. It’s not just for tech experts; it’s for everyone.
To learn how to protect yourself online, keep exploring the in-depth articles in the VPN Guides section on Safelyo and check out our detailed VPN reviews.