So, what is split tunneling VPN? Think of it as a smart traffic controller for your internet connection. It gives you the power to choose which apps go through the secure, encrypted VPN tunnel and which ones use your regular, faster internet connection directly.
In our connected world, a standard VPN can feel like a blunt instrument. You enable it for security, but then face frustrating trade-offs: your streaming service buffers endlessly, you can’t access your home printer, or your online banking site blocks you. These are the exact issues that make many users turn their VPN off, leaving them exposed.
With over a decade of hands-on experience in network security, I’ve seen countless users struggle with this exact dilemma. Split tunneling isn’t just a technical feature; it’s the elegant solution that bridges the gap between airtight security and everyday convenience.
In this guide, you’ll discover:
- How split tunneling works with a simple, clear analogy.
- The real-world situations where this feature is a lifesaver.
- The different types of split tunneling and which one is for you.
- A balanced look at the security risks and how to manage them.
Stop compromising between speed and safety. Let’s dive in and unlock a smarter way to use your VPN.
1. What is split tunneling, and how does it actually work?
To truly grasp split tunneling, you first need to understand what your VPN does by default. Most of the time, when you connect to a VPN, it creates a ‘full tunnel’.
Imagine your internet connection is a busy highway. A full tunnel is like directing every single vehicle – your work emails, your Netflix stream, your online banking, even your connection to your home printer – onto a single, armored, high-security expressway. Everything is encrypted and protected, which is great for security. However, this one-lane-for-all approach can cause traffic jams, slowing everything down.
This is where split tunneling comes in. It’s like having a smart GPS that gives you a choice. You can create a special exit ramp on that secure expressway.

With this feature, you can decide which “vehicles” need the armored route and which can take the faster, local roads. For instance, you can send your sensitive banking traffic through the secure VPN tunnel while letting your Netflix stream use your regular, faster internet connection to avoid buffering. You’re essentially splitting your traffic between two paths: The encrypted VPN tunnel and your open internet connection.
From my experience testing dozens of VPNs, this is the feature that separates a good VPN from a great one. It’s the difference between having a powerful security tool and having a powerful tool that you actually enjoy using every day because it doesn’t get in your way.
2. When you actually need VPN split tunneling
Theory is one thing, but where does split tunneling truly make a difference in your daily online life? Let’s move past the technical definitions and look at some practical scenarios where this feature goes from a “nice-to-have” to an absolute necessity.
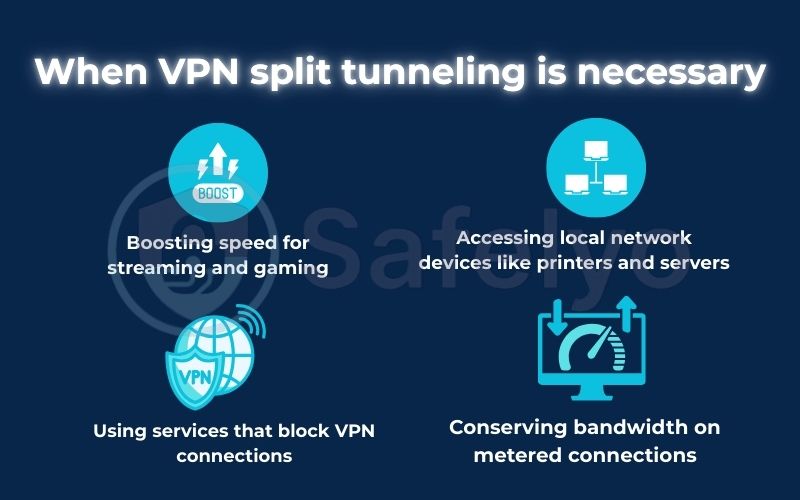
2.1. Boosting speed for streaming and gaming
Meet Bob. He wants to watch a show that’s only available on the US library of Netflix, so he connects his VPN to a server in New York. But at the same time, his friends are inviting him to a match in an online game hosted on a local European server.
Without split tunneling, he has a problem. If he keeps the VPN on, his gaming connection will be routed all the way to New York and back, causing horrible lag and a high ping. If he turns it off, he loses access to the show he wants to stream.
This is the perfect scenario for split tunneling. Bob can configure his VPN to send only the Netflix app’s traffic through the US server. Meanwhile, his game connects directly to the internet, giving him the low latency he needs to play competitively. This is a classic use case for both split tunneling for streaming and split tunneling for gaming.
From our own testing at Safelyo, we’ve seen ping times in games like Valorant and Apex Legends drop by as much as 50-70ms when bypassing the VPN. In the world of competitive gaming, that’s the crucial difference between landing a headshot and getting eliminated.
2.2. Accessing local network devices like printers and servers
Now, let’s consider Alice, who works from home. Her company requires her to be connected to the corporate VPN all day to access sensitive files on the company server. But when she tries to print a report, her computer can’t find the wireless printer sitting just a few feet away from her in the same room.
Why? Because the “full tunnel” VPN sends all her network traffic to her company’s servers, completely isolating her from her own local home network.
I can’t tell you how many times I’ve seen people frantically disconnect from their secure work VPN just to print one page, creating an unnecessary security risk. With split tunneling, Alice can simply tell her VPN to exclude traffic going to her local network devices. This way, she can stay securely connected to her work server while seamlessly printing documents, accessing a personal NAS drive, or streaming media from a local server.
>> You may also be interested in: How to set up a NAS for home use: Step-by-step guide 2025
2.3. Using services that block VPN connections
Have you ever been browsing securely with your VPN on, only to be blocked when you try to log into your online banking website? This is incredibly common. Many financial institutions and some government services see logins from unfamiliar, distant IP addresses (like those from a VPN server) as a potential security threat and will deny access.
Instead of turning off your VPN entirely and exposing all your other browsing activity, you can use split tunneling. Simply add your banking app or the bank’s website URL to the exclusion list.
This way, your bank sees your regular, trusted IP address and lets you in, while the rest of your internet activity – your research, social media, and general browsing – remains safely encrypted behind the VPN. It’s about working with, not against, the security measures of other services.
2.4. Conserving bandwidth on metered connections
This is a lifesaver for anyone using a connection with a data cap, like a mobile hotspot or a limited home internet plan. VPN encryption adds a small amount of data “overhead” to your traffic. While it’s usually negligible on an unlimited connection, it can add up quickly on a metered one.
Let’s say you’re working while traveling and using your phone as a hotspot. You want to protect your sensitive work emails and messages, but you don’t want to waste your precious gigabytes encrypting a high-definition YouTube video you’re watching during your break.
With split tunneling, you can configure your VPN to only route the essential, low-data apps (like Outlook and Slack) through the encrypted tunnel. You can let the data-hungry apps (like YouTube and TikTok) use the standard, unencrypted connection, ensuring you protect what’s important without draining your data plan.
3. The different types of split tunneling explained
Now that you see the power of split tunneling, it’s helpful to know that it comes in a few different flavors. The type your VPN you offer will determine how precisely you can control your traffic.
3.1. App-based split tunneling
This is the most common and user-friendly version you’ll find. As the name suggests, it lets you choose which specific applications (apps) will use the VPN tunnel.
For example, you could set your BitTorrent client and your web browser to always route through the VPN for privacy, while allowing your online game launcher and Spotify to connect directly to the internet for maximum speed. It’s simple, intuitive, and covers the needs of most users.
3.2. URL-based split tunneling
This type offers a more granular level of control. Instead of routing an entire app, you can choose which specific websites (URLs) go through the VPN. This is also sometimes called a “browser extension” feature.
Imagine your web browser is the only app you want to manage. You could configure it so that only netflix.com and bbc.co.uk are routed through the VPN to unblock content, while every other site you visit, like Google or YouTube, uses your regular, faster connection. It’s incredibly precise.
3.3. Inverse split tunneling
This works in the opposite way. Instead of choosing what goes inside the VPN tunnel, you choose what stays outside. With inverse split tunneling, all your internet traffic is routed through the VPN by default, except for the specific apps or websites you add to an exclusion list.
I find this is the best approach for people who want a “set it and forget it” security mindset. You get maximum protection by default and only have to make exceptions for a few trusted apps that have issues with VPNs, like your online banking app or a local network device.
Safelyo’s Pro Tip
For most users, app-based split tunneling offers the best balance of simplicity and control. URL-based is powerful but can be tedious to manage if you visit many sites. Inverse split tunneling is ideal if your main priority is security and you only have a few specific apps you need to exclude from the VPN.
To make it even clearer, here’s a simple table to help you compare:
| Type | How It Works | Control Level | Best For… |
|---|---|---|---|
| App-based | You select which apps use the VPN. | Good | General use, balancing security and speed for specific applications like torrenting or gaming. |
| URL-based | You select which websites use the VPN. | Very Precise | Unblocking specific streaming sites or news sources without slowing down the rest of your browsing. |
| Inverse | Everything uses the VPN by default, except what you exclude. | High Security | Users who want maximum security by default and only need to bypass the VPN for a few trusted apps or sites. |
4. Is split tunneling safe? A balanced look at the pros and cons
Split tunneling is an incredibly useful feature, but it introduces a trade-off. By routing some of your traffic outside the encrypted VPN tunnel, you are consciously choosing convenience over absolute protection for that specific data. So, is split tunneling safe? The answer is: It depends entirely on how you use it.
To make the decision easier, here’s a clear, side-by-side look at the trade-offs:
Pros (The Good)
- Access local and remote networks at once.
- Boosts speed for gaming, streaming & downloads.
- Saves data on metered connections (e.g., mobile hotspot).
- Bypasses services that block VPNs (like banking apps).
Cons (The Risks)
- Unencrypted traffic is visible to your ISP.
- Vulnerable to snooping on untrusted public Wi-Fi.
- Potential for DNS leaks if not configured correctly.
- Requires careful management to avoid security gaps.
Let’s break down the benefits and risks in a straightforward way.
4.1. The benefits (pros)
As we’ve covered, the advantages are clear and practical. To summarize, here are the main benefits of split tunneling:
- Simultaneous Access: You can access foreign content (like a streaming library) and local services (like your printer) at the same time.
- Optimized Speed: You can get maximum speed for data-heavy activities like gaming or downloading by routing them outside the VPN.
- Bandwidth Conservation: You can save precious data on metered connections by only encrypting essential, low-data traffic.
- Bypass VPN Blocks: You can use services like online banking that often block connections from VPN IP addresses.
4.2. The security risks (cons)
It’s crucial to be aware of the potential downsides. The primary split tunneling risk is straightforward: Any traffic you route outside the VPN tunnel is not encrypted by the VPN.
This means that traffic is exposed to the same risks as if you weren’t using a VPN at all. Your internet service provider (ISP) can see the websites you visit, and if you’re on an unsecured public Wi-Fi network (like at a café or airport), a skilled hacker on the same network could potentially intercept that unencrypted data.
Another potential issue is a DNS leak. In some poorly configured setups, even if an app’s traffic goes through the VPN, its DNS requests (the “phonebook” of the internet) might leak out through the regular connection, revealing your browsing activity. Reputable VPN providers have built-in DNS leak protection to prevent this, but it’s a risk to be aware of.
My rule of thumb at Safelyo, and what I tell everyone who asks, is simple: Evaluate the network you are on. When I’m working from my trusted home office network, I use split tunneling all the time to balance performance and security. But the moment I connect to the Wi-Fi at a coffee shop, hotel, or airport, I switch to full-tunnel mode. No exceptions.
Safelyo’s Security Rule
Never use split tunneling on a network you don’t trust. On public Wi-Fi, always use the full tunnel setting for maximum protection. Reserve split tunneling for your trusted home or office network where the risk of local snooping is minimal.
5. How to enable and configure split tunneling
Getting split tunneling up and running is usually a quick process. While the interface of every VPN app is unique, the core steps and considerations are largely the same. Let’s walk through the process, from finding the setting to understanding where it’s available.
5.1. Step-by-step instructions
Here is a general guide that applies to most top-tier VPN apps that offer this feature:
- Open your VPN application and make sure you’re logged in.
- Find the Settings or Preferences menu. Look for the universal gear icon (⚙️) or a menu icon (≡).
- Locate the Split Tunneling feature. It may be listed under a “Connection,” “General,” or “Advanced” tab. Some brands give it a unique name, like “Whitelister” or “Bypasser.”
- Enable the feature using the toggle switch provided.
- Choose your split tunneling mode. The app will ask you to define your rule. The most common options are:
- Route only selected apps through the VPN (Standard).
- Route all apps through the VPN except for selected ones (Inverse).
- Select your apps. A list of your device’s applications will pop up. Simply check the boxes for the apps you want to apply the rule to.
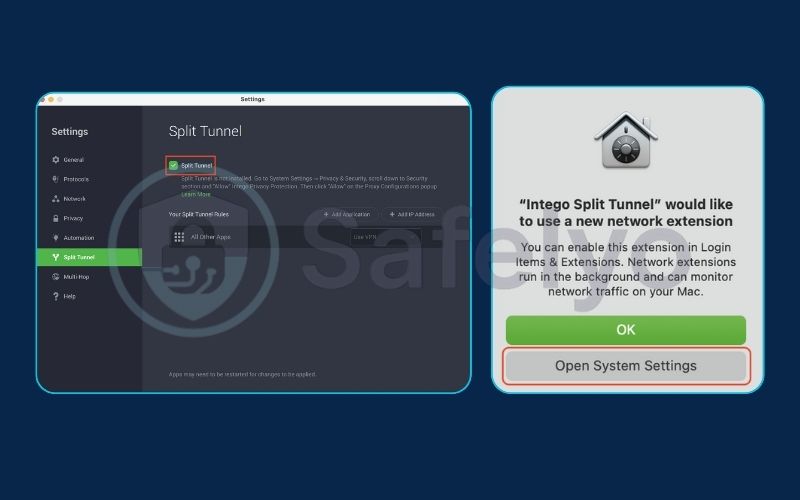
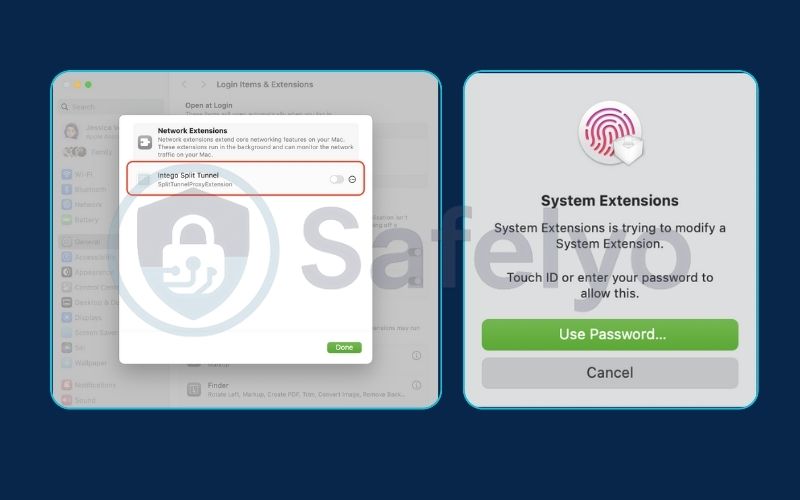
Once configured, the changes should take effect on your next connection, routing your traffic according to your new preferences.
5.2. A quick note on operating system availability
Before you go hunting for the setting, it’s crucial to know that split tunneling isn’t universally available on every device. Its functionality often depends on the operating system’s built-in architecture.
Windows & Android
On these platforms, the feature is widely supported and works exceptionally well. Almost every major VPN provider with split tunneling offers a full-featured version for Windows and Android. From personal experience, it’s a stable and reliable tool on both.
macOS & iOS
Support here is far more limited and less common. Apple’s strict networking framework makes it technically challenging to implement split tunneling. While a few providers offer workarounds, they may come with limitations. If this is a must-have feature for your Mac or iPhone, always verify its availability and functionality with the VPN provider beforehand.
6. Who should (and shouldn’t) use split tunneling?
After exploring all the details, you might be wondering: “Is this feature actually for me?” It’s a great question. While powerful, split tunneling isn’t the right choice for every situation or every user.
Here’s a quick summary to help you decide.
You should definitely use split tunneling if you are:
- A remote worker who needs constant access to both secure company resources via VPN and local network devices like a home printer or server.
- A gamer or streamer who wants to unblock geo-restricted content while simultaneously maintaining the lowest possible ping for competitive play or smooth streaming.
- A user on a limited data plan (like a mobile hotspot) who needs to conserve bandwidth by only encrypting the most sensitive applications.
- A power user who loves to fine-tune their setup for maximum efficiency and control over their digital life.
You should probably stick to a full tunnel if you are:
- A journalist, activist, or anyone handling highly sensitive information. In these cases, the risk of even a minor data leak outweighs any benefit of speed or convenience. Maximum security is paramount.
- Someone who frequently uses unsecured public Wi-Fi at places like airports, cafes, or hotels. These networks are prime targets for snoops, and you should always encrypt 100% of your traffic.
- A user who prioritizes simplicity above all else. If you don’t face speed issues or problems accessing local devices, the “set it and forget it” nature of a full tunnel provides excellent protection with zero configuration.
7. FAQ about split tunneling VPN
We’ve covered a lot of ground, but you might still have some specific questions. Here are quick, direct answers to the most common queries we receive about VPN split tunneling.
What is split tunneling VPN?
In short, VPN split tunneling is a feature that lets you divide your internet traffic. It gives you the choice to send some of your apps or websites through the secure VPN connection, while others connect directly to the internet.
What is the difference between full tunneling and split tunneling?
Full tunneling sends 100% of your internet traffic through the encrypted VPN server for maximum security. Split tunneling is more flexible; it lets you choose which specific apps or websites use the VPN, while the rest use your regular internet connection.
What is the main advantage of using a split tunnel VPN configuration?
The main advantage is flexibility. It allows you to get the best of both worlds: you can maintain high security for sensitive activities while enjoying maximum speed and local network access for everything else.
Is VPN split tunneling good or bad?
It’s neither inherently good nor bad – it’s a powerful tool. It’s good when you use it correctly on a trusted network to balance speed and security. It can be bad if you use it carelessly on an unsecured public network, as it leaves some of your traffic exposed.
Why disable split tunneling?
You should disable split tunneling (and use a full tunnel) whenever maximum security is your top priority. This is crucial when you’re connected to an untrusted public Wi-Fi network (like at an airport or café) or when you’re handling highly sensitive personal or professional information.
Do all VPNs have split tunneling?
No, it’s typically considered a premium feature. Most high-quality paid VPN services offer it, but you’re unlikely to find it in free or very basic VPNs. Always check the feature list before you subscribe to a service.
Can split tunneling make my internet slower?
Quite the opposite. The traffic you route outside the VPN will run at your normal, faster internet speed. By offloading data-heavy activities from the VPN server, split tunneling actually improves your overall connection performance compared to a full tunnel setup.
How do I know if split tunneling is working correctly?
A simple test is to open two different web browsers. Configure one browser to use the VPN and the other to bypass it. Then, go to a “what is my IP address” website in both browsers. If it’s working, you should see two different IP addresses.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and using what is split tunneling VPN is a powerful way to move beyond a one-size-fits-all approach to your digital security. It’s a feature that puts you in the driver’s seat, allowing you to tailor your connection to your exact needs, moment by moment.
To sum up the key points to remember:
- It offers the best of both worlds: targeted security for sensitive data and optimal performance for everything else.
- It solves common VPN frustrations like being blocked by banking sites or being unable to access local devices like printers.
- While there are minor risks, they are easily managed by using the feature on trusted networks and reverting to a full tunnel on public Wi-Fi.
- It’s an indispensable tool for remote workers, gamers, streamers, and anyone who wants granular control over their connection.
Ultimately, split tunneling transforms your VPN from a simple shield into a smart, adaptable tool. Ready to take full control of your connection? Explore the expert-tested guide from Safelyo to the best VPNs with split tunneling to find the perfect service for you. Mastering this feature is a key step in building your knowledge in the VPN Guides category.