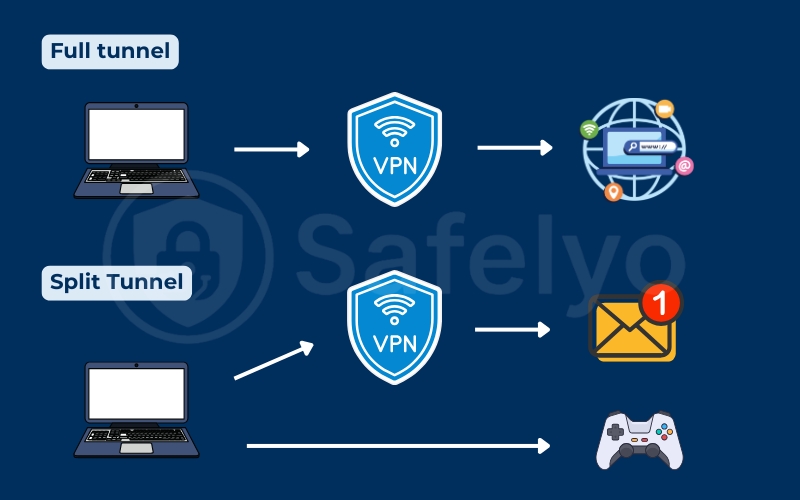
The VPN tunnel style that routes only certain types of traffic is split tunneling. It lets you decide which apps or websites use the encrypted VPN route and which ones connect directly through your regular internet line.
Imagine you want your browser to stay protected under a VPN for privacy, but you prefer your online games or video calls to use the local network for better speed. Split tunneling allows exactly that flexibility without disconnecting the VPN entirely.
This feature differs from full-tunnel routing, where every packet travels inside the encrypted tunnel. By letting some traffic skip the VPN, you can balance security and performance based on what you’re doing online.
Key takeaways:
- The answer to which VPN tunnel style routes only certain types of traffic is split tunneling.
- Split tunneling routes selected apps or sites through the VPN while others go directly online.
- It improves speed and latency but can expose non-tunneled traffic.
- Always test DNS and IP leaks after enabling it to ensure privacy.
1. Which VPN tunnel style routes only certain types of traffic?
The VPN tunnel style that routes only specific types of traffic is split tunneling. It gives users precise control over how their devices send data online. Instead of forcing all connections through a VPN server, split tunneling lets you apply encryption only where it matters.
In a full-tunnel VPN, every bit of data goes through the encrypted channel. That means higher security but sometimes slower speeds because even local or trusted traffic takes the long route. Split tunneling changes that rule by allowing you to define which apps or IP ranges should bypass the tunnel.
For example, many users keep their web browsers connected through the VPN for privacy while letting online games or streaming apps use direct access to avoid lag. Business users might connect to internal servers via VPN but still access local printers or shared drives normally.
Split tunneling delivers flexibility and performance without fully giving up encrypted protection when configured correctly.
2. How split tunneling works
Split tunneling works by deciding which network requests travel through the encrypted VPN tunnel and which use your normal internet connection. The VPN client applies routing rules to separate traffic before it leaves your device.
When you enable split tunneling, the VPN software updates your system’s routing table. Each application or destination is assigned a path. For example, your browser might be directed through the VPN, while a game or update service is set to use your direct internet line.
DNS handling also plays a role. Apps routed through the VPN use the secure DNS provided by the VPN server, while excluded apps rely on your local or ISP DNS. This split can lead to leaks if not configured carefully, which is why some users perform DNS and IP tests after setup to confirm isolation.
Split tunneling can work across major VPN protocols such as OpenVPN, WireGuard, and IKEv2. The function itself is implemented at the client level, not built into a single protocol. Whether you use a Windows, macOS, or mobile client, the principle stays the same: only selected data flows through the VPN.
3. Pros and cons of using split tunneling
Split tunneling gives users more control over their internet routing, but it also introduces privacy and security trade-offs. Understanding both sides helps decide when to use it safely.
Main pros of split tunneling:
- Faster speed and lower latency: Only essential apps go through the VPN, reducing encryption load and improving performance.
- Selective privacy: You can keep sensitive apps under VPN protection while allowing local or low-risk services to connect directly.
- Bandwidth savings: Sending only chosen traffic through the VPN reduces strain on your internet connection.
- Access to local devices: You can print, share files, or use NAS devices without disconnecting the VPN.
Main cons of split tunneling:
- Risk of data exposure: Traffic that bypasses the tunnel is not encrypted, which may reveal your IP or browsing activity.
- Potential DNS leaks: If routing or DNS rules are misconfigured, private data may reach public resolvers.
- Compliance problems: Some workplaces or regulated networks require full VPN routing for monitoring and data protection.
- Higher setup complexity: Users must understand which apps to include or exclude to avoid security gaps.
Split tunneling is smart to use when performance matters more than complete encryption. Examples include streaming region-locked shows, playing online games, or accessing local servers while staying partly protected.
However, avoid it on public Wi-Fi or shared networks, where exposed traffic can be intercepted easily.
4. FAQs about which VPN tunnel style routes only certain types of traffic
Split tunneling can be confusing for new VPN users, especially when deciding if it is safe or effective. These short answers explain how it works and when to use it.
Is split tunneling the same as policy-based routing?
They are related but not identical. Policy-based routing is a broader method used by network administrators to direct packets based on rules, often at the router level. Split tunneling applies similar logic inside a VPN client, letting users choose which apps or websites follow the encrypted tunnel and which connect normally.
Does split tunneling weaken encryption?
No, split tunneling does not weaken the encryption of traffic that stays inside the VPN. Only data excluded from the tunnel is unencrypted, behaving the same as regular internet traffic. As long as sensitive apps remain within the VPN route, encryption strength is not affected.
Will split tunneling improve gaming or streaming performance?
Yes, it often helps. By sending games or video streams directly through the internet instead of the VPN tunnel, latency drops and buffering becomes less likely. Many users enable split tunneling specifically to balance security for private apps with smoother gaming or streaming performance.
Is split tunneling safe on public Wi-Fi?
It can be risky. On open or public networks, any app that bypasses the VPN sends data without encryption. Hackers or local snoopers can see that traffic. For full protection, disable split tunneling and use a complete VPN connection when connected to public Wi-Fi.
Can I split by domain as well as by app?
Yes, some VPNs let you split traffic by domain as well as by app, but support depends on the provider.
Domain-based split tunneling (also called URL or destination routing) lets you decide which websites or hostnames go through the VPN.
For example, you can send *.work.com through the VPN while keeping streaming sites on your normal connection.
Most consumer VPNs only support per-app rules, while enterprise VPNs or custom routers can manage domain-level or IP-based policies through routing tables or DNS rules.
5. Conclusion
The answer to which VPN tunnel style routes only certain types of traffic is split tunneling. It allows selected apps or websites to use the secure VPN tunnel while leaving other traffic to follow the normal internet route. This balance gives users both privacy and performance when used correctly.
Summary of key points:
- Split tunneling routes chosen traffic through the VPN and leaves the rest outside.
- It increases speed and lowers latency for non-sensitive apps.
- Incorrect configuration can cause IP or DNS leaks.
- Use full-tunnel routing on public Wi-Fi or in regulated networks.
From personal testing, enabling split tunneling on a Windows laptop helped speed up large file downloads while keeping my cloud storage app fully encrypted through the VPN.
Before relying on split tunneling daily, always test your setup using a DNS or IP leak tool. Proper verification ensures that privacy remains intact while you enjoy faster connections.
For more simple and practical tech explanations, visit the Privacy & Security Basics section at Safelyo to explore other VPN and cybersecurity guides.