One of the first questions many people have is, Does a VPN encrypt data? The simple answer is yes. In fact, encryption isn’t just a feature – it’s one of the most fundamental and important functions of any trustworthy VPN service.
In today’s digital world, an unencrypted connection is like an open postcard. Whether you’re connecting at a coffee shop or just browsing at home, your personal information can be exposed to your Internet Service Provider (ISP), network administrators, and cybercriminals.
As a security analyst, I’ve seen firsthand how unencrypted connections on public Wi-Fi can lead to stolen passwords and compromised accounts. Understanding that a VPN’s primary job is to create an encrypted shield isn’t just for tech experts; it’s a fundamental piece of digital self-defense for everyone today.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover:
- How a VPN uses encryption to create a secure ‘tunnel’ for your data.
- Exactly what data does a VPN encrypt (and are there any exceptions)?
- What “military-grade encryption” really means (and why it’s so strong).
- The crucial difference between a VPN and encryption itself.
Don’t leave your data exposed. Let me demystify the technology that keeps you safe and show you how to take control of your online privacy.
1. The core concept: VPN and encryption explained
To truly understand how a VPN protects you, we first need to get a clear picture of its two most important components: The VPN itself and the encryption that powers it. They work together, but they are not the same thing.
1.1. What is VPN encryption?
At its heart, VPN encryption is the process of taking your readable data and scrambling it into a secret code. Think of it as a highly advanced digital cipher.
Only your device and the VPN server you’re connected to have the special “encryption key” needed to unscramble that code and read the original information. This ensures that even if a hacker intercepts your data, they won’t see anything useful. If your ISP intercepts your data, the result is the same. All they will see is a meaningless jumble of characters.
The gold standard for this process, used by virtually all top-tier VPNs, is AES-256, an incredibly powerful encryption algorithm that we’ll demystify later in this guide.
1.2. VPN vs. encryption: What’s the difference?
This is a common point of confusion. From my experience, the easiest way to understand the VPN vs encryption difference is with a simple analogy:
- Encryption is the unbreakable safe. It’s the process of taking your valuable data and locking it inside a secure container so no one can read it.
- A VPN is the armored truck service. It’s the entire system that picks up your locked safe, transports it securely through a private route (VPN tunneling), and delivers it safely to its destination.
Encryption is a specific technique, whereas a VPN is a comprehensive tool that utilizes this technique as its primary security measure. You can have encryption independently (such as with HTTPS websites), but a secure VPN cannot exist without encryption.
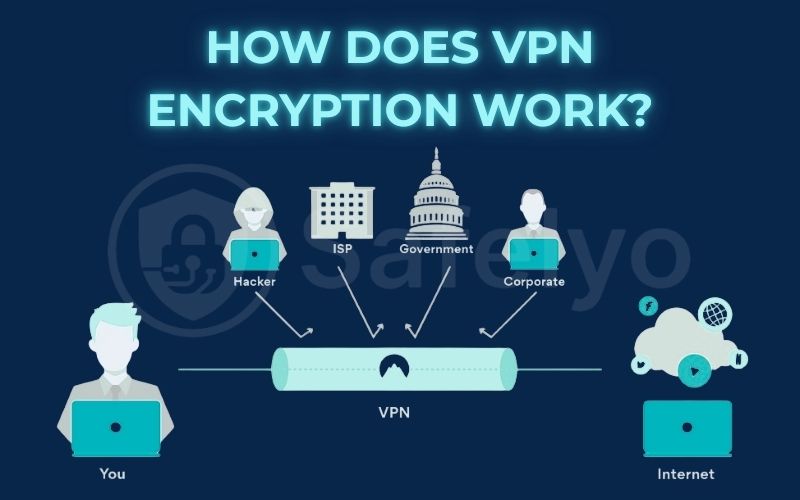
1.3. How does VPN encryption work? The secure tunnel explained
So, how does the “armored truck” actually work? The VPN encryption explained here is a process that happens in a fraction of a second when you hit ‘Connect’.
- The Secure Handshake: The moment you connect, your device and the VPN server perform a “secret handshake.” They securely exchange and agree upon the encryption key that will be used for the session.
- Encryption in Action: Now, every piece of data you send – a website request, an email, a password – is instantly scrambled into unreadable code (ciphertext) on your device using that key.
- The VPN Tunnel: This encrypted data is then sent through a secure “tunnel.” VPN tunneling is the process of placing your encrypted data packets inside another, outer packet. This effectively hides your data from the public internet, just like an armored truck hides its cargo from view.
- Decryption and Forwarding: The encrypted data arrives at the VPN server. The server uses the key to decrypt your request, then sends it on to the website you want to visit. The process happens in reverse when you receive data back.
2. Does a VPN encrypt data? And which?
This is a critical question. Knowing that a VPN encrypts your data is one thing, but understanding the scope of that protection is essential. Does it protect just your browser, or everything on your device?
2.1. Does a VPN encrypt all internet traffic?
For a properly configured, high-quality VPN, the answer is yes. When the VPN is active, it is designed to capture and encrypt all internet traffic that leaves and enters your device.
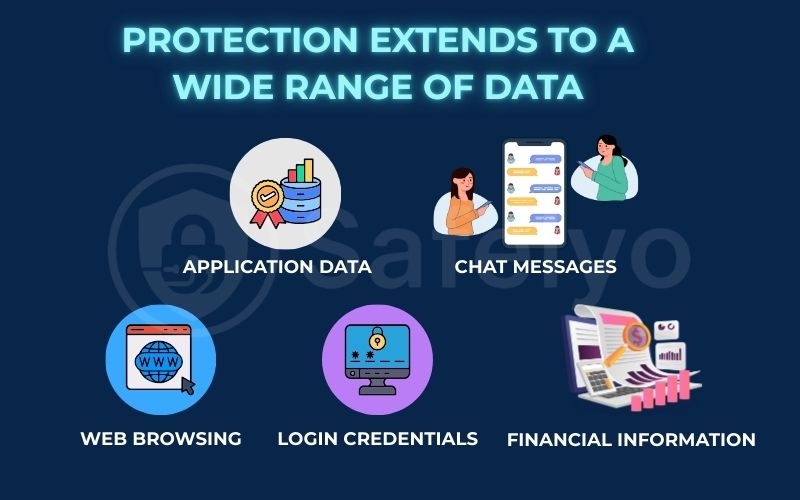
This isn’t just limited to your web browser. This protection extends to a wide range of data, including:
- Your Web Browsing: The websites you visit, the articles you read, and the searches you make.
- Login Credentials: Your usernames and passwords when you log into websites and apps.
- Financial Information: Your credit card details and banking information during online transactions.
- Application Data: Data from other apps on your device that connect to the internet, such as email clients, cloud storage apps (like OneDrive or Dropbox), and even some games.
- Chat Messages: Communications from internet-based messaging apps.
Essentially, what data does a VPN encrypt? If it’s data being sent from or to your device over the internet, a full VPN connection is designed to encrypt it.
2.2. The exception: Understanding split tunneling
Now, there is one major exception to the “all traffic” rule, but it’s a feature, not a flaw. Many modern VPNs offer a feature called split tunneling.
I use split tunneling all the time in my own setup, and it’s incredibly useful. It allows you to choose which apps use the encrypted VPN tunnel and which apps connect to the internet directly.
To use our analogy, split tunneling lets you decide which “mail” gets sent via the secure armored truck and which gets sent via the regular postal service.
- Accessing Local and Foreign Services Simultaneously: You could route your web browser through a UK VPN server. This allows you to watch BBC iPlayer. At the same time, your banking app can connect directly to your local bank. This helps avoid triggering a security alert.
- Maximizing Speed: You might only want to encrypt your sensitive browsing traffic while allowing a high-bandwidth activity like online gaming to connect directly for the lowest possible ping.
It’s an advanced feature that gives you more control, but it’s important to remember that any traffic you exclude from the VPN tunnel will not be encrypted by the VPN.
3. Demystifying VPN encryption standards
When you’re comparing VPN services, you’ll be bombarded with technical-sounding terms. Understanding what these mean is key to choosing a service that offers genuine security, not just marketing hype. As an analyst, my job is to cut through this jargon for you.
3.1. What is military-grade encryption?
You will see this phrase everywhere. So, what is military-grade encryption?
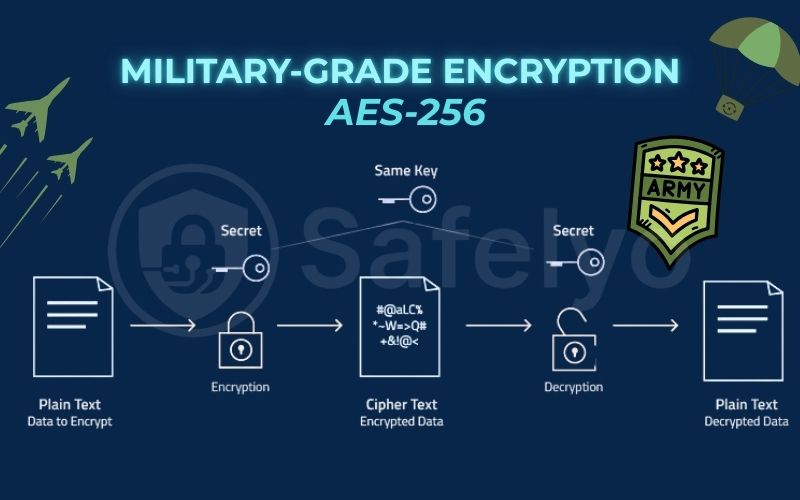
First, you should know that “military-grade” is a marketing term, not an official technical standard. However, what it refers to is very real and very powerful: AES-256.
- AES stands for Advanced Encryption Standard, and it’s the global gold standard for symmetric encryption.
- The 256 refers to the length of the encryption key.
Why is a 256-bit key so strong? The number of possible combinations for a 256-bit key is astronomical – it’s a number with 78 digits. To put that in perspective, a modern supercomputer, the fastest machine on Earth, would need to run for billions of years to guess the correct key through a “brute-force” attack.
It’s called “military-grade” because AES-256 is the same encryption standard trusted by the U.S. government and security agencies worldwide to protect classified and top-secret information. When a VPN says they use it, it means they are using a genuinely unbreakable standard of encryption.
3.2. A quick look at VPN protocols (the engines of encryption)
If AES-256 is the unbreakable safe, the VPN protocols are the blueprints for the armored truck. They are the set of rules and instructions that a VPN uses to create a secure connection and implement encryption.
You don’t need to be an expert, but knowing the names of the most modern and secure protocols is helpful. In any quality VPN app, you’ll see these options:
- OpenVPN: The long-standing, battle-tested industry standard. It’s incredibly reliable and secure, the “workhorse” of the VPN world.
- WireGuard: The modern superstar. It’s famous for its incredible speeds, lightweight design, and state-of-the-art cryptography. Many VPNs have adopted it as their new default.
- IKEv2/IPsec: Known for being very stable and fast, especially on mobile devices. It’s excellent at reconnecting instantly when you switch from Wi-Fi to cellular data.
My advice to beginners is simple: most top-tier VPNs will automatically select the best protocol for you. But seeing these names in the settings is a great sign that your provider is using modern, secure technology to protect you.
4. Does a VPN protect you from hackers?
This is one of the most common and important questions people ask. The honest answer is: Yes, but only from specific types of attacks. A VPN is an incredibly powerful security tool, but it is not a magic shield that makes you immune to all online threats. As a security analyst, I believe it’s crucial to be transparent about what a tool can and cannot do.
4.1. Where a VPN is your best defense
A VPN is most effective at protecting you from attacks that rely on intercepting your internet traffic.
- Public Wi-Fi Attacks: This is where a VPN shines. When you’re at a coffee shop, airport, or hotel, you’re sharing a network with strangers. A hacker on that same network can use tools to perform a “Man-in-the-Middle” attack, essentially spying on your unencrypted traffic to steal passwords, credit card numbers, or other sensitive data. Because a VPN encrypts everything, all the hacker will see is scrambled, useless code. This is the single most important reason I never use public Wi-Fi without a VPN.
- ISP Snooping: Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can see every website you visit. A VPN’s encrypted tunnel completely blocks this, protecting your browsing history from your provider.
>> Read more: Can VPN be hacked? The honest answer & 4 things to do
4.2. Where a VPN cannot protect you
A VPN secures your connection, but it cannot protect your device or your decisions.
- Malware and Viruses: If you download a malicious file or get infected with a virus, a VPN can’t stop it. The encrypted file will be delivered to your computer just as securely as if it were in a safe. For this, you need a high-quality antivirus program.
- Phishing Attacks: A VPN cannot prevent you from being tricked. If you receive a fake email from your “bank” and you willingly click a link to a fake website and enter your login details, you have given your password away. A VPN can’t protect you from deception.
- Data You Publicly Share: If you post personal information on social media, a VPN offers no protection.
The Bottom Line:
A VPN is an essential part of a layered security strategy. It’s the “armored truck” for your data in transit. However, you still need a strong lock on your front door, like antivirus software. Additionally, smart personal habits, such as avoiding phishing, are essential for true security.
5. FAQ about the VPN encryption
We’ve covered the core concepts of VPN encryption. Here are some quick, direct answers to the most common follow-up questions we receive.
Do VPNs actually encrypt your data?
Yes, absolutely. The core function of any reputable VPN service is to encrypt your data. It scrambles all the internet traffic leaving your device, making it unreadable to your ISP, network administrators, or any snoopers on a public Wi-Fi network.
What kind of encryption do VPNs use?
Most top-tier VPNs use the AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) with a 256-bit key, often referred to as “military-grade encryption.” This is a symmetric encryption standard that is considered practically unbreakable by modern computers.
How do I know if my VPN is encrypted?
If you are using a legitimate, well-known VPN service, you can be confident your connection is encrypted. The VPN protocols they use (like OpenVPN, WireGuard, or IKEv2) have encryption built into their core function. You can also look for a VPN icon in your device’s status bar, which indicates an active, encrypted connection.
Is VPN 100% untraceable?
No, no tool can make you 100% untraceable. A high-quality, no-logs VPN provides a very high level of privacy and makes it extremely difficult to trace your online activity back to you. However, it cannot protect you from things like logging into your personal Google account or posting personal information on social media.
What is the difference between encryption and hashing?
Encryption is a two-way process; data that is encrypted can be decrypted with the correct key. In contrast, hashing is a one-way process; you can convert data into a hash, but you cannot reverse the hash to its original form. Hashing is used to verify data integrity and securely store passwords, rather than for sending secret messages.
What’s the difference between plaintext vs. ciphertext?
Plaintext and ciphertext are fundamental concepts in encryption. Plaintext refers to the original, readable data, while ciphertext is the scrambled, unreadable data produced after encryption is applied.
6. Conclusion
So, does a VPN encrypt data? The answer is an emphatic yes, and that encryption is the cornerstone of its power to protect your online privacy. It’s the fundamental process that transforms your sensitive information from an open postcard into a locked, armored safe.
Understanding this core function is the key to appreciating the value of a high-quality VPN in a world where our data is constantly traveling across public networks.
- A VPN creates a secure tunnel for your data and scrambles it using powerful encryption standards like AES-256.
- It protects all your internet traffic, keeping you safe from hackers on public Wi-Fi and snooping by your ISP.
- While incredibly powerful against traffic interception, a VPN is not an all-in-one security solution and should be paired with good antivirus software and smart browsing habits.
- “Military-grade encryption” is a marketing term for the highly secure AES-256 standard, trusted by security experts worldwide.
Understanding that encryption is the foundation of a good VPN empowers you to make a more confident and informed choice when selecting a service to guard your digital life.
Now that you understand how a VPN protects you, your next step is to explore the different types of VPNs available. Explore the expert reviews and guides in the Privacy & Security Basics section of Safelyo to find the right provider for your needs.