Are you trying to keep your online activities secure and private, only to be met with the frustrating reality of your VPN (Virtual Private Network) constantly disconnecting? It’s like having a bodyguard who wanders off during important activities like streaming or secure browsing. You’re not alone; this common hiccup can disrupt working securely from home or your binge-watching sessions.
The truth is, figuring out why does my VPN keep disconnecting can feel like a bit of a tech puzzle. It could be anything from a wobbly internet connection at your router to a mischievous setting on your device or even an issue with your Virtual Private Network provider itself. But don’t you worry, that’s exactly why I’m here.
I have years of experience in network troubleshooting. I have helped many people secure their digital defenses. In that time, I have seen and fixed many connection problems.
In this guide, I’ll cut through the confusion and explore:
- The key reasons your Virtual Private Network connection might be unstable.
- Practical, step-by-step solutions you can try right now.
- When it might be time to consider if your VPN service is the culprit.
Let me help you pin down those elusive causes and get your VPN back to being the reliable shield it’s meant to be. Let’s dive in and stop those annoying drops!
1. Why does my VPN keep disconnecting?
Before we roll up our sleeves and dive into the fixes, it’s crucial to understand what we’re dealing with. When we talk about a VPN that “keeps disconnecting,” we mean frequent dropouts after a successful connection, leaving your data exposed and your activities visible. This is different from a situation where your Virtual Private Network won’t connect at all from the get-go.
If you’re struggling to even establish that first handshake with the VPN server, you might find our guide on ‘Why is my VPN not connecting?’ more helpful.
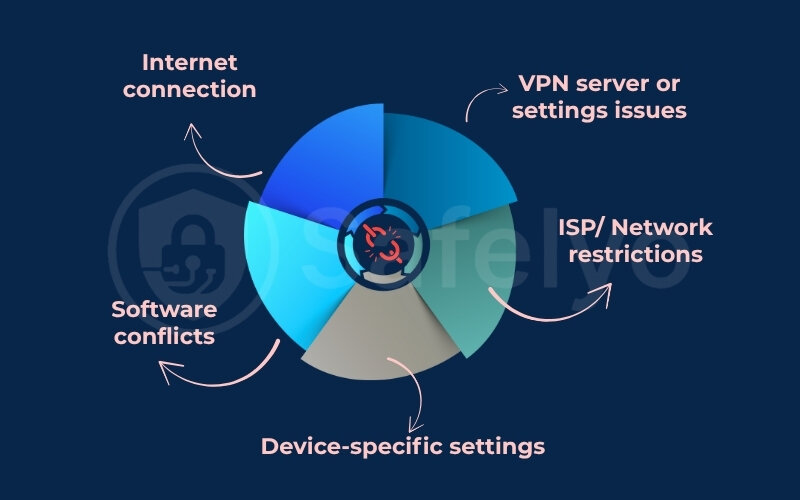
So, why does your seemingly cooperative Virtual Private Network suddenly decide to take a break? The culprits can be varied, often falling into a few main categories:
- Your own internet connection stability: The VPN relies on your underlying internet; if that’s shaky, your VPN will be too.
- VPN server or settings issues: Problems with the server you’re connected to, or how your VPN client is configured.
- Software interferences on your device: Other programs, especially security software, might be interfering.
- ISP (internet service provider) or network restrictions: Sometimes, your ISP or the network you’re on doesn’t play nice with VPNs.
- Device-specific settings: An aggressive battery saving mode can inadvertently cut off your VPN.
Pinpointing the exact reason your VPN connection is unstable is the first step towards a lasting solution. Understanding these potential factors will save you a lot of guesswork.
Users can spend hours on complex network analysis. The problem is often a simple battery saver feature on their phone. This feature closes the VPN app to conserve power. It’s these “aha!” moments that highlight why a systematic approach is key.
1.1. The usual suspect of an unstable internet connection
Think of your VPN connection as a passenger in a car – your internet connection is the car itself. If the car keeps sputtering or stalling, the passenger isn’t going anywhere smoothly. Similarly, if your connection is unstable due to weak Wi-Fi, high latency, or potential ISP blocking, your Virtual Private Network will inevitably struggle to maintain a stable link.
This is often the very first place I look when someone tells me their VPN keeps disconnecting. So, how can you tell if your base internet is the problem child?
- Run a speed test: Use online tools like Speedtest by Ookla or Fast.com. Don’t just look at download/upload speeds; pay close attention to ping (latency) and jitter. High or fluctuating ping can indicate instability. Some tools also report packet loss, which is a major red flag for Virtual Private Network stability.
- Perform a ping test: Open Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (macOS) and type ping google.com -t (for Windows) or ping google.com (for macOS). Let it run for a few minutes. If you see “Request timed out” messages frequently or widely varying response times, your connection is unstable.
- Observe your non-VPN connection: Try streaming shows or downloading files without the VPN active. If you still experience slowdowns or drops, the issue likely lies with your internet service itself. You might notice your internet drops even when the Virtual Private Network tries to connect, which is a strong indicator.

If your internet seems shaky, try these basic fixes:
- Restart your modem and Wi-Fi router: The classic “turn it off and on again” works wonders on your home router.
- Move closer to your Wi-Fi router: A weak signal from the router can cause intermittent drops.
- Try a wired Ethernet connection: If possible, plugging directly into your router bypasses Wi-Fi issues entirely and offers a more stable link.
- Check with your ISP: If problems persist, there might be an issue with your internet service provider that needs their attention.
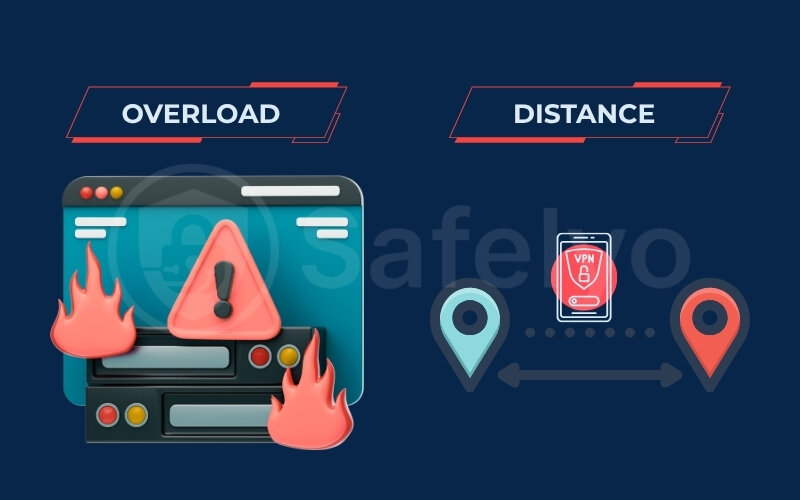
1.2. VPN server issues: Overload or distance
Sometimes, your internet connection might be rock solid, but the VPN server you’re trying to use is the one having a bad day. Imagine trying to board an overcrowded bus. Too many people connecting for activities like streaming can cause slowdowns. A distant server can also make your Virtual Private Network connection slow or unstable.
Two main server-related factors can cause your VPN to disconnect frequently:
Server overload
Popular VPN servers, especially during peak hours, can become congested with too many users. This strain can lead to slower speeds, increased latency, and, you guessed it, disconnections as the server struggles to handle the traffic. This is particularly common with free VPN services that often cram more users and their simultaneous connections onto fewer servers.
Server distance
The physical distance between you and the Virtual Private Network server matters. Connecting to a server across the world creates a long journey for your data. This increases the chance of network hiccups that can disrupt the VPN tunnel.
From personal experience, I once worked with a client who was experiencing frequent VPN disconnects during video calls. After reviewing his setup, we discovered his VPN app was auto-connecting him to a faraway server in Europe, despite him being based in Asia.
As soon as he manually switched to a closer server with lower latency, the disconnection issues stopped completely. This simple fix made a big difference – and highlighted how something as basic as server location can drastically impact VPN stability.
Luckily, addressing these issues is usually straightforward:
- Switch to a different server: This is the easiest fix. Most VPN apps have a list of server locations. Try connecting to a server that is geographically closer to you. If you suspect overload, try a different server in the same country or a nearby one. I often find that picking a server in a less “obvious” city, rather than a major hub like New York or London, can sometimes yield better stability.
- Look for server load indicators: Some VPN clients display the current load (percentage of users or bandwidth capacity) or ping time for each server. Opt for servers with lower load and lower ping.
- You should consider your VPN provider: Do you have frequent disconnects on many different servers? This may mean their server infrastructure is not robust enough, especially with free services.
1.3. Conflicts with other software or firewall settings
Your computer or mobile device is a bustling ecosystem of applications, and sometimes, they don’t all play nicely together. Other software, particularly security programs with strict configurations, can mistakenly identify your VPN’s activity as suspicious and interfere with its connection, leading to those annoying drops. It’s like having a security guard who’s a bit too jumpy and keeps detaining your friendly VPN messenger.
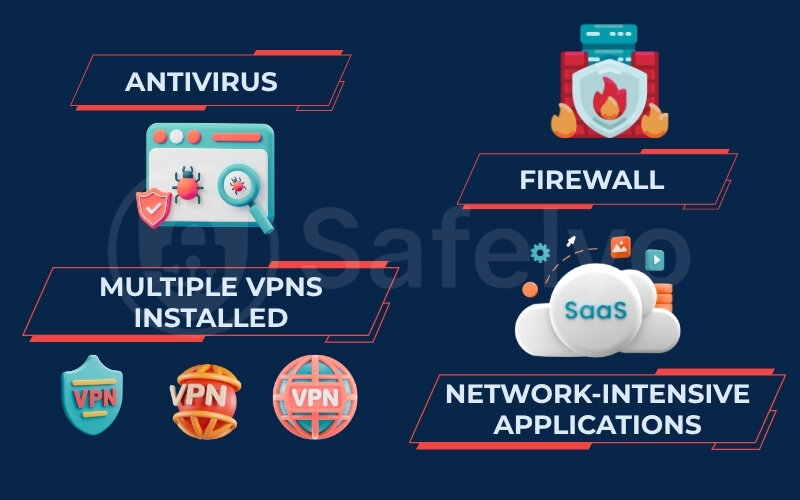
Here’s how these conflicts can manifest and what to do:
Security aoftware interference
Some antivirus suites include their own firewall or network monitoring features that can clash with your VPN. They might block the VPN’s attempts to create a secure tunnel or cut off its traffic.
- Solution: Temporarily disable your anti-malware software (just for a few minutes to test, and be sure to re-enable it!). If the VPN stays connected, you’ve found your culprit. Then, dive into your anti-malware software settings and look for an option to add your VPN application to an “exceptions” or “whitelist.” This tells the anti-malware software to trust your VPN.
Firewall blocks
Your operating system’s built-in firewall (like Windows Defender Firewall or macOS Firewall) or a third-party firewall could be blocking the ports or the specific tunneling protocol your VPN uses.
- Solution: Similar to anti-malware software, you can test by temporarily disabling the firewall. If that helps, you’ll need to configure the firewall to allow your VPN client or specific VPN protocols/ports. For example, in Windows Defender Firewall, you’d typically go to “Allow an app or feature through Windows Defender Firewall” and add your VPN.
Multiple VPNs installed
If you have more than one VPN client installed, even if you’re only actively using one, their background processes or network drivers can sometimes conflict.
- Solution: Uninstall any VPN clients you are not actively using.
Other network-intensive applications
Less commonly, other apps that heavily manage or modify network traffic (like certain download managers or network optimizers) could potentially cause issues.
When I troubleshoot for others, I often find a common issue. Firewall or anti-malware software settings are frequently the “silent culprits.” They interfere with connections without giving clear error messages. Creating those exceptions is usually a one-time fix that brings lasting stability.
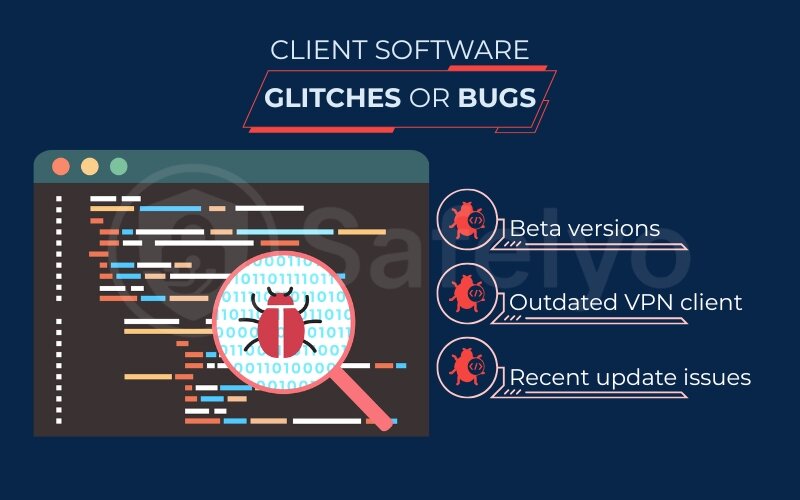
1.4. VPN client software glitches or bugs
Sometimes, the problem isn’t with your internet, the server, or other software – the issue might lie within the VPN client software itself. Like any piece of software, VPN applications can have their own software issues or bugs, especially in newer versions or if you’re running an outdated client. These glitches can manifest as unexpected disconnections, even if everything else seems fine.
Think of it like a minor defect in a tool; it might work most of the time, but occasionally, it just doesn’t perform as expected.
- Outdated VPN client: If you haven’t updated your VPN app in a while, you might be running a version with known bugs that have since been fixed. Developers regularly release updates to patch vulnerabilities and fix performance issues, including those that could cause connection drops.
- Recent update issues: Ironically, sometimes a brand-new update can introduce new, unforeseen bugs. This is less common with reputable providers who do thorough testing, but it’s not unheard of.
- Beta versions: If you’re using a beta version of a VPN client, expect a higher chance of encountering bugs and instability. That’s the nature of beta testing.
What can you do?
- Check for updates: The first and simplest step is to ensure your VPN client is updated to the latest stable version. Usually, you can find a “Check for Updates” option within the app’s settings or menu.
- Visit provider forums/communities: Before you pull your hair out, do a quick search on your VPN provider’s official forum or community pages (like Reddit subs dedicated to that VPN). See if other users are reporting similar disconnection issues with the current version. This can quickly tell you if it’s a widespread problem or something specific to your setup.
- Consider a rollback (if possible and necessary): In rare cases, if a new update is clearly the cause, some VPNs or operating systems might allow you to revert to a previous, more stable version of the app. This is generally a last resort.
I always advise keeping your software, especially security-related tools like VPNs, up to date. But if you start experiencing issues right after an update, checking community feedback is a smart move before assuming the problem is on your end.
2. How to fix VPN disconnecting: Practical solutions
Now that we’ve explored some of the common culprits behind why your VPN keeps dropping, it’s time to get hands-on with the fixes. Don’t feel overwhelmed if the list of potential causes seems long – often, a simple tweak is all it takes to get your connection back on solid ground.
I’ll walk through a series of practical solutions, starting with some of the easiest and most common adjustments you can make within your VPN client and on your device. I recommend trying these steps one by one and testing your VPN connection after each change to see if the issue is resolved.
This systematic approach will help you pinpoint exactly what works for your setup. Let’s get that VPN stable!
2.1. Change VPN protocol
Your VPN client uses a specific tunneling protocol, which is a set of rules, to establish a secure connection. Some common VPN protocols include OpenVPN (which can run over UDP or TCP), IKEv2, and WireGuard.
Different protocols have different strengths regarding speed, security, and stability, and some work better on certain networks than others. If your VPN keeps disconnecting, the currently selected tunneling protocol might be struggling with your network conditions.
OpenVPN (UDP vs. TCP)
UDP is generally faster but can be less reliable on unstable networks. If you’re using OpenVPN (UDP) and experiencing dropouts, try switching to OpenVPN (TCP). TCP has error-checking mechanisms that make it more resilient to packet loss, though it might be slightly slower. I often find this switch alone resolves many disconnection issues, especially on less stable Wi-Fi.
IKEv2
Known for its stability and speed, especially on mobile devices, as it handles network changes (like switching from Wi-Fi to mobile data) very well. A good option to try if available.
WireGuard
A newer protocol that’s gaining popularity for its excellent speed and modern security. It’s generally very stable, but if it’s the default and you’re having issues, trying an older, more established protocol like OpenVPN might be worth a shot.
How to change it
Look for “Protocol” settings within your VPN app, usually under “Connection,” “Advanced,” or “Settings.” Select a different protocol from the list and try reconnecting.

2.2. Disable battery saving or network optimization features
Modern operating systems often have an aggressive battery saving mode, especially on mobile devices (Android and iOS). A battery saving mode can sometimes identify those apps like VPN on iPhone or VPN on Android apps as “high-consumption” background processes. It shuts them down or restrict their network access to conserve power, leading to your Android VPN keeps disconnecting or iPhone VPN keeps disconnecting. Similar network optimization features might exist on desktops, too.
Android
Go to Settings > Apps > [Your VPN App] > Battery. Look for options like “Battery optimization” and set it to “Not optimized” or “Unrestricted.” The exact path might vary slightly depending on your Android version and manufacturer.
iOS
iOS is generally less aggressive, but ensure “Background App Refresh” is enabled for your VPN app (Settings > General > Background App Refresh). Also, avoid using Low Power Mode if VPN stability is critical, as it restricts background activity.
Windows/macOS
Check your power plan settings. Ensure that network adapters are not set to be turned off to save power, especially in custom or battery-saving power plans.
I have found a very common fix for Android users. Whitelist the VPN app from your device’s battery optimization settings. This helps when the VPN drops after inactivity or the screen is off.
2.3. Update or reinstall your VPN client and device OS
Outdated software is a common source of all sorts of tech gremlins, including VPN connection instability. Bugs in an older VPN client version or even your device’s operating system can lead to unexpected disconnections.
Developers are constantly releasing patches and updates to fix these issues. Similarly, if your VPN on computer keeps disconnecting, an OS update or a VPN client update might be the key.
- Update VPN client: Open your VPN app and look for an “Update,” “Check for Updates,” or “About” section. Download and install the latest version.
- Update Operating System:
- Windows: Go to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update.
- macOS: Go to System Settings/Preferences > General > Software Update.
- Android/iOS: Go to Settings > System > System update (Android) or Settings > General > Software Update (iOS).
- If updating the VPN client fails, try reinstalling it. You might have a corrupted installation. Uninstall the client, restart your device, and then reinstall the latest version. This can clear out any problematic configuration files.
Keeping your digital toolkit sharp with the latest updates is good practice not just for stability, but for security too.

2.4. Check for ISP throttling or blocking
While it’s not always the case, some Internet Service Providers (ISPs) aren’t big fans of VPNs. They might throttle (slow down) VPN traffic or even actively block certain VPN protocols or ports, which can certainly cause your VPN to disconnect frequently.
This is sometimes done to manage network congestion or discourage activities they can’t monitor. Signs your ISP might be interfering:
- VPN disconnections happen more frequently on your home network than on other networks (like mobile data or a friend’s Wi-Fi).
- Specific VPN protocols consistently fail while others might work.
- Your internet speed drops dramatically only when the VPN is connected.

What to try:
- Use obfuscated servers (if your VPN offers them): Some VPNs have special servers or “stealth mode” features designed to disguise VPN traffic as regular HTTPS traffic, making it harder for ISPs to detect and block.
- Switch to TCP Port 443: This is the port standard HTTPS traffic uses. Many VPNs allow you to configure OpenVPN to run over TCP port 443, which is less likely to be blocked by ISPs.
- Contact your ISP: This can be a long shot, as they might not admit to throttling or blocking VPNs. However, you can inquire about any known issues with VPN connectivity on their network.
It’s a bit of a cat-and-mouse game sometimes, but using obfuscation features is often the most effective way I’ve found to deal with suspected ISP meddling.
2.5. Restart your devices and router
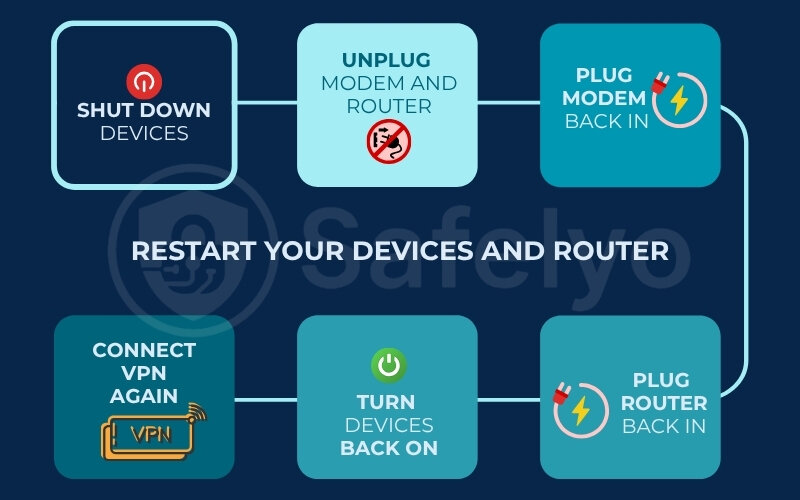
This might sound overly simple, but the good old “turn it off and on again” trick is a staple in IT troubleshooting for a reason. Restarting your computer, smartphone, and your home router can clear out temporary glitches, flush DNS caches on the router, resolve minor software conflicts, and refresh your network connections.
Here’s the best way to do it:
- Shut down your computer/smartphone.
- Unplug your modem and your router. Wait for about 30-60 seconds. This allows them to fully reset.
- Plug your modem back in first. Wait for all its lights to stabilize (usually 1-2 minutes).
- Plug your router back in. Wait for its lights to stabilize.
- Turn your computer/smartphone back on.
- Try connecting your VPN.
It’s always worth a try before diving into more complicated steps. I can’t count the number of times Safelyo readers (and I!) have reported that this simple sequence magically fixed a VPN that randomly disconnects when all other complex solutions failed.
2.6. Checking device-specific settings (Windows, macOS, Android, iOS)
Beyond general fixes, each operating system has its own quirks and settings that can affect VPN stability. If your VPN keeps disconnecting on a specific device, it’s worth diving into these platform-specific areas.
Windows:
- Network Adapter Drivers: Outdated or corrupted network adapter drivers are a common culprit. Go to Device Manager, find your network adapter (Wi-Fi or Ethernet), right-click, and select “Update driver.” You might also need to download the latest driver from the manufacturer’s website.
- Windows Event Viewer: Check the System or Application logs in Event Viewer around the time of disconnection for any error messages related to your VPN client or network services. This can provide clues.
- Interfering Network Services: Some third-party network management tools or even certain Windows services (like the “Internet Connection Sharing” if misconfigured) could interfere.
macOS:
- Network Preferences: Go to System Settings/Preferences > Network. Ensure your active network connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet) is stable. You can try creating a new “Location” profile to reset network configurations and DNS settings.
- VPN Profiles: If you’ve manually configured VPN profiles, ensure they are set up correctly. Remove and re-add the profile if necessary.
Android:
- Always-on VPN: For critical connections, Android has an “Always-on VPN” feature (Settings > Network & internet > VPN > [select your VPN] > tap the gear icon). This can help maintain the connection, though it might not fix underlying drop issues. Also, ensure “Block connections without VPN” is enabled if you want to prevent data leaks during momentary drops.
- App Permissions: Double-check that your VPN app has all necessary permissions, especially for background activity and network access.
iOS:
- Connect on Demand: In your VPN settings (Settings > General > VPN > [tap ‘i’ next to your VPN config]). The “Connect On Demand” feature can be useful but sometimes, if misconfigured or if the network changes frequently. It might lead to perceived disconnections as it tries to re-establish.
- Reset Network Settings: If all else fails on iOS, Settings > General > Transfer or Reset iPhone > Reset > Reset Network Settings can resolve stubborn issues, but be aware this erases all Wi-Fi networks and passwords.
I often help people with VPNs that keep timing out. Investigating OS-specific settings often reveals the root cause. This is especially true after general fixes have failed to work.
>> Read more: How to set up a VPN on any device in 3 simple steps
3. When to consider switching your VPN provider
You’ve patiently worked through all the recommended steps. You’ve checked your internet, tweaked settings, updated software, and maybe even had a friendly chat with your router. Yet, despite your best efforts, your VPN keeps disconnecting, and the frustration is mounting. If this sounds like your situation, it might be time to consider a hard truth: The problem might not be with your setup, but with your VPN provider itself.
While many VPN disconnections are due to local factors, there are definitely times when the service you’re paying for (or using for free) is the weakest link. Here are some signs that your current VPN provider might be the reason my VPN won’t stay connected:
- Persistent server issues: If you consistently experience disconnections regardless of which server you choose, or if servers are frequently unavailable or extremely slow, it points to an unreliable server infrastructure.
- Outdated protocols or limited options: A good VPN provider stays current with the latest, most stable protocols (like WireGuard) and offers alternatives (like OpenVPN TCP/UDP, IKEv2) for flexibility. If your provider only offers old protocol options, they might not be investing enough in technology that improves connection stability.
- Poor customer service: When you reach out for help with disconnections, do you get generic, unhelpful replies, or no reply at all? A provider unwilling or unable to help you with their own service is a red flag. I’ve found that responsive and knowledgeable support can make a huge difference.
- Known issues with the provider: A quick search online for “[Your VPN Provider Name] disconnecting issues” might reveal many other users experiencing similar problems. This could indicate a systemic issue with the service.
- Lack of advanced features for stability: Features like a reliable kill switch (to prevent data leaks if the VPN drops), split tunneling (to route only some traffic through the VPN), or obfuscation (to bypass VPN blocks) can indirectly contribute to a more stable and usable experience. If your provider lacks these, they might not be focused on a robust user experience.
- Especially with free VPNs: While tempting, free VPNs are notorious for overloaded servers, limited bandwidth, fewer server locations, and a general lack of resources to maintain a stable network. If you’re using a free service and facing constant drops, upgrading to a reputable paid provider is often the most effective solution.
If you’ve exhausted other problem-solving options and several of these signs resonate with you, it’s a strong indicator that switching providers could significantly improve your VPN experience. Don’t keep battling a service that consistently fails you.
If you suspect your provider is the issue, it might be a good time to check out Safelyo’s reviews of top reliable Best VPN services. We rigorously test VPNs for performance, stability, and features, which can help you find a service that won’t leave you hanging.
You may also be interested in this article: Why is my VPN not connecting? 8 causes and how to fix them
4. FAQ about VPN disconnections
We’ve covered a lot of ground on why your VPN might be playing hide-and-seek with your connection. Here are answers to some of the most common questions Safelyo readers and I encounter regarding VPN disconnections:
Why does my VPN disconnect after a few minutes?
Most often, this is due to aggressive battery-saving settings on your device closing the VPN app. Other causes include an unstable internet connection or overloaded VPN servers. Check power settings first.
Can using a free VPN cause more disconnections?
Yes, very likely. Free VPNs often have overcrowded servers, fewer resources, and limited stability features, making your vpn keep dropping more frequently than paid services.
How do I know if my ISP is interfering with my VPN?
It’s tricky, but signs include: VPN drops only on your home network, or specific protocols failing. Trying VPNs with “obfuscation” or using TCP port 443 can help bypass this.
Does changing VPN protocol affect security?
Generally, no, if you stick to modern protocols like OpenVPN, IKEv2, or WireGuard. Switching between them is more about finding stability and compatibility for your network, not a major security compromise.
What should I do if my work VPN keeps disconnecting?
Contact your company’s IT department immediately. The issue could be related to your account’s device limit. They manage the device limit and can troubleshoot issues specific to their setup and policies. Don’t try to fix it yourself without their guidance.
Why does my VPN disconnect when my computer sleeps or my router assigns a new IP?
This is usually due to power management settings that disconnect network adapters to save power. Check your OS “Power Options” or “Energy Saver” settings, and your network adapter properties.
How do I stop VPN from disconnecting?
Systematically troubleshoot: check your internet, try different VPN servers/protocols, review your DNS settings, update software, check firewall/antivirus conflicts, and disable aggressive battery savers for the VPN app.
How do I keep my VPN on all the time?
Use your VPN app’s “launch on startup” and “auto-reconnect” features. Android’s “Always-on VPN” setting also helps. However, you must first fix the underlying disconnection issues.
Why does my VPN keep turning on and off?
This “cycling” often indicates an unstable connection that drops, then the VPN’s auto-reconnect tries, and it drops again. Focus on stabilizing the initial connection by addressing internet, server, or software interference issues.
Why is my VPN stopping?
This could be due to any reason discussed: unstable internet, server problems, software conflicts, battery savers, outdated software, or ISP interference. Use the checklist in this article to find the cause.
5. Conclusion
Having your “why does my VPN keep disconnecting” issue can indeed be a persistent annoyance, disrupting your online privacy and security. However, as we’ve explored, the reasons can range from your local internet setup to specific software settings or even the VPN service itself. The good news is that most of these problems are solvable with a bit of methodical troubleshooting.
Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways to remember:
- Always check your fundamental network connection first – a shaky base means a shaky VPN.
- Experiment with different VPN servers and protocols; what works for one network might not for another.
- Keep your VPN client software and device operating system updated to patch bugs and improve compatibility.
- Investigate potential conflicts from firewalls, antivirus software, or even aggressive battery-saving modes.
- Don’t underestimate the simple power of a full restart for your devices and router.
- If all else fails after thorough troubleshooting, be prepared to evaluate if your current VPN provider is the root cause.
By patiently applying the solutions and insights shared in the VPN Guides category on Safelyo, you can significantly enhance the stability of your VPN connection. And if you determine it’s time for a more reliable service, remember to consult Safelyo’s detailed VPN reviews. It can make an informed choice and ensure your online experience is both secure and seamless. Stay safe out there!