Ever wondered how does a VPN work to create a private shield for your online activities? At its core, it creates a secure, encrypted tunnel for your traffic, hiding your activity from your ISP, advertisers, and anyone trying to monitor you.
In today’s digital age, where we work, do online shopping, and socialize online, understanding this technology isn’t just for the tech-savvy. It’s a fundamental step towards protecting your online identity and achieving true online privacy, whether you’re using public wi-fi at a café or just browsing from your couch at home.
At Safelyo, our mission is to make digital security simple. We believe the best way to protect yourself is to understand the tools you use. That’s why this guide is designed for beginners. We’ll skip the complex jargon and use simple analogies to explain exactly what happens behind the scenes.
-
Authentication
-
Tunneling
-
Encryption
-
IP masking
It’s time to move from uncertainty to confidence. Let me walk you through the entire process, so you can take back control of your digital security.
1. Before the VPN: Understanding your unprotected connection
To truly appreciate what a VPN (Virtual Private Network) does, let’s first look at what your internet connection looks like without one. Think of your online activity – every website you visit, every search you make – as writing on a postcard.
This postcard is handed to your internet service provider (ISP), who acts as the mail carrier, delivering it to its destination. The problem? It’s an open postcard. The message isn’t sealed in an envelope.
This means your ISP can see exactly which websites you’re visiting. But it doesn’t stop there. If you’re using a public network, like the WI-FI at a coffee shop, airport, or school, the network administrator can also get a peek. Your data travels across these public networks completely exposed, making it easy for third parties to intercept and read.
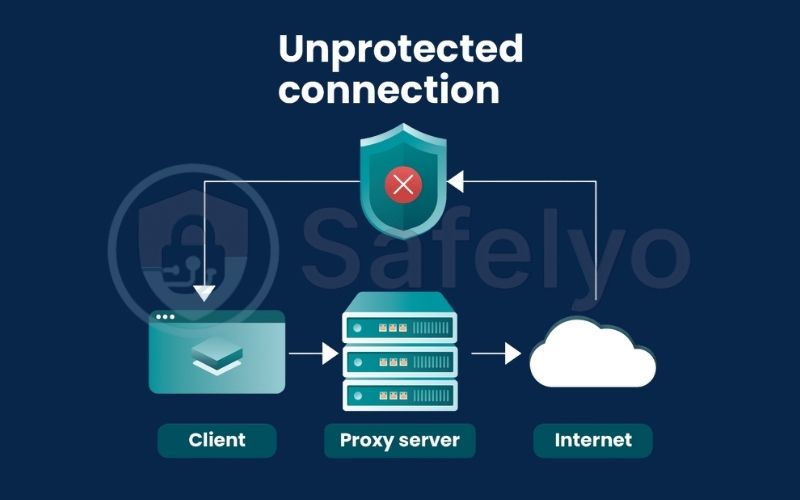
This is the default state of the internet: A system with very little built-in online privacy. Because your data isn’t encrypted (scrambled), your ISP, network administrators, and potential snoops can see where you go online. This leaves your IP address and digital footprint completely exposed.
But what if you could put that postcard inside a locked, armored box instead? That’s where a VPN comes in.
2. What is a VPN?
That locked, armored box we mentioned? That’s exactly what a VPN is. It’s the solution to the open postcard problem and the core of this guide on VPN for beginners.
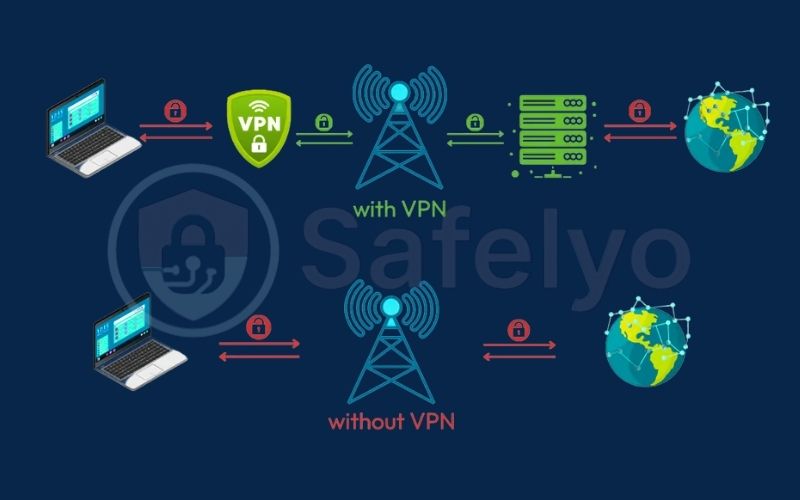
Let’s continue with our analogy. Instead of handing over that open postcard, a VPN lets you do this:
- You place your data (the postcard) inside a locked metal safe.
- This safe is then put into an armored car (the VPN connection).
- The armored car drives on a private, secure highway directly to a secure sorting facility (the VPN server) before your message is delivered to its final destination.
This process prevents data leakage, as no one along the route – not your ISP, not a hacker lurking on the network – can peek inside. They can only see the armored car, not the contents or the final destination. This is VPN explained simply: it creates a secure connection for you, even when you’re using a public network.
For years, I admit I used public wi-fi without a second thought. The ‘armored car’ concept was a lightbulb moment for me. It wasn’t about being paranoid; it was about understanding that my default connection was built for convenience, not privacy. Knowing a simple app could create a private path for my data changed how I view online security, and it’s the easiest way Safelyo can explain it.
3. Key benefits of using a VPN
Okay, so a VPN acts like a digital armored car. But why does this actually matter for you day-to-day? Understanding how is great, but the why is what makes a VPN an essential tool. It translates that technical process into real-world data protection and freedom.
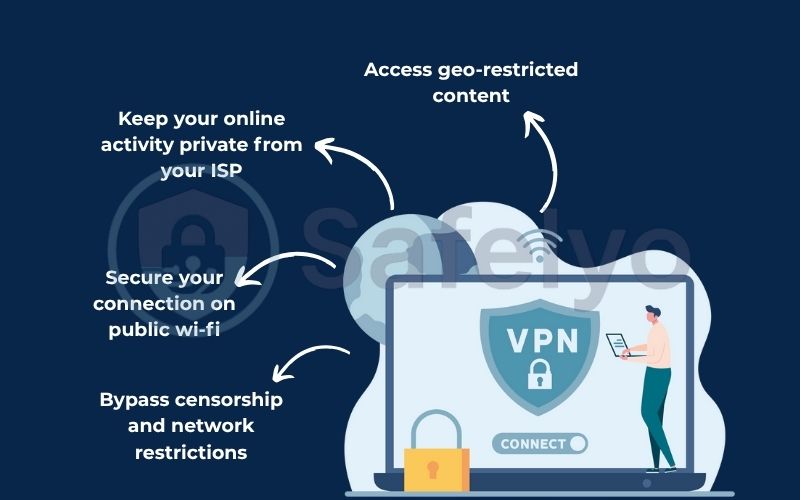
Here are the key benefits you get from using a VPN:
Secure your connection on public wi-fi.
This is a big one for me. I often work from coffee shops or airports, and those free wi-fi networks are notoriously insecure. They’re a prime hunting ground for cyber criminals and data thieves. A VPN encrypts everything you do, turning that risky public hotspot into your own private and secure connection. It’s like putting up soundproof walls in a crowded room.
Keep your online activity private from your ISP.
Without a VPN, your internet provider knows every single website you visit, how long you stay, and what you do. With a VPN, your traffic is hidden inside that encrypted tunnel. They can see that you’re using data, but they can’t see what you’re doing or where you’re going online. They can no longer log or sell your browsing history to advertisers.
Access geo-restricted content.
Have you ever been traveling and tried to watch a show on your favorite streaming services, only to be met with a “not available in your region” error? It’s frustrating. A VPN solves this by letting you connect to a server in your home country, making it look like you’re browsing from your own living room.
>> This is a huge benefit for streaming fans. We can link here to a future guide like the Best VPNs for Streaming.
Bypass censorship and network restrictions.
That news site your office network blocks? Or the social media app your school restricts? A VPN can often get around these local blocks by tunneling your traffic past the network’s firewalls, giving you unfiltered access to the open internet.
>> Read more:
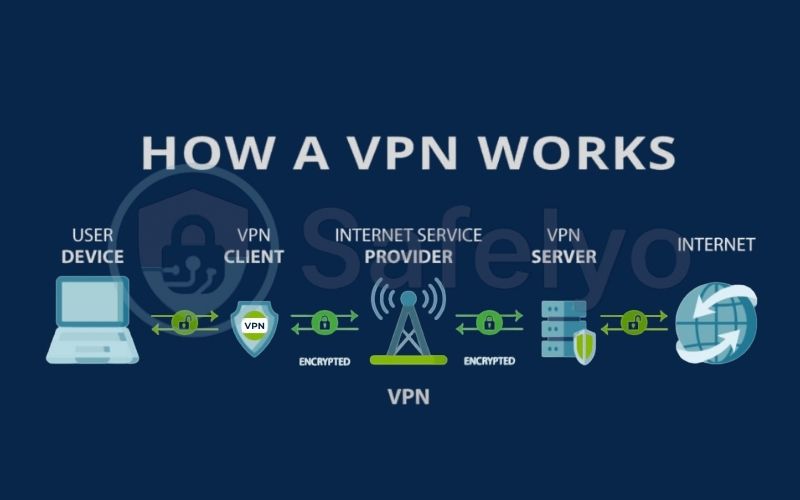
4. The 4-step core process of how a VPN works
Now that you understand the why, let’s pull back the curtain on the how. While the technology is complex, the process can be broken down into four straightforward steps.
How does a VPN work in 4 steps to protect your online privacy and data
- Authentication
- Tunneling
- Encryption
- IP masking
This is the nitty-gritty of how a VPN works, explained in a way that anyone can understand.
4.1. Step 1: Authentication – The digital handshake
The moment you click “Connect” on your VPN app, the first thing that happens is a process called authentication. It’s like a secret handshake between your device and a remote server.
Think of it like being a VIP at a club. Before the bouncer lets you into the exclusive area, they check your ID to make sure you’re on the list. In the digital world, your VPN app presents its credentials, sometimes secured with two-factor authentication, to prove it’s a legitimate subscriber. The server then confirms its identity back to your app. This secure “handshake” ensures you are connecting to a trusted server and not a malicious imposter. Only after both sides are verified can the process continue.
4.2. Step 2: Tunneling – Creating your private highway
Once the handshake is complete, your VPN gets to work building your private highway. This is known as creating a VPN tunnel.
Imagine the regular internet is a chaotic, public city street, with everyone’s traffic mixed together. The VPN tunnel is like an instant, private, underground passage that appears just for you. This tunnel seals off your internet traffic from all the other data traveling on the public network. Everything you do from this point forward travels inside this protected passage, shielded from view.
4.3. Step 3: Encryption – Scrambling your data into a secret code
This is where secure data transfer is guaranteed: VPN encryption. Building a private tunnel is great, but what makes it truly secure is that everything inside is scrambled into an unreadable code.
It’s like writing a secret message, then using a special decoder ring to turn it into gibberish. Anyone who intercepts the message without the matching decoder ring just sees a meaningless jumble of characters. This is what a VPN does to your data – your emails, passwords, and browsing activity.
This isn’t just any simple code. Reputable VPNs use AES-256 encryption, which is the same military-grade standard used by governments and banks to protect classified information.
The rules and methods for this process are called VPN protocols. You might see names like OpenVPN, WireGuard, IKEv2, or older options like L2TP and PPTP. Avoid PPTP if possible. I like to think of them as different shipping services for your data package. OpenVPN is the time-tested global standard, incredibly reliable and universally trusted. WireGuard is the modern, lightning-fast courier, offering top-tier security with incredible speed.
4.4. Step 4: IP masking – Hiding your true location and identity
The final step is giving you a new digital identity. Every device connected to the internet has a unique IP address, which is like the home address for your device. This IP address reveals your general location to every website and service you connect to.
When your encrypted data travels through the VPN tunnel and reaches the VPN server, the server strips away your real IP address and replaces it with its own VPN IP address. Now, when your data continues to its final destination (like google.com), the website sees the request coming from the VPN server, not from you.
Here’s a simple example: If you’re in Vietnam but connect to a VPN server in New York, websites will see you as if you’re browsing from New York. This location spoofing is exactly how a VPN hides your IP address, protecting your location and helping you access content.
>> Read more:
5. What a VPN does not protect?
At Safelyo, we believe in full transparency. A VPN is a powerful tool, but it’s not a magic bullet that solves every digital threat. To use it effectively, it’s just as important to understand its limitations.
I’ve talked to many users who get a false sense of invincibility once they install a VPN. Let’s clear up some common misconceptions.
It is not an antivirus.
This is the most important distinction. A VPN protects your data in transit between your device and the internet. An antivirus protects your device from malicious files that are already on it.
Simple Example: Think of our armored car again. The VPN (the car) securely delivers a sealed package to your door. But if that package contains a bomb (a virus), the armored car has done its job perfectly. You still need a security system at your house (an antivirus) to scan the package and make sure it’s safe to open.
It does not stop phishing attacks.
A VPN encrypts your connection, but it can’t stop you from making a bad decision. If you receive a fake email from “your bank” and click a link to a fraudulent website, the VPN will securely connect you to that fake site.
I’ve seen phishing emails that look incredibly real. A VPN doesn’t prevent you from willingly giving your password away on a convincing-looking scam page. Your vigilance is the best defense here.
It does not block all tracking.
A VPN is fantastic at hiding your IP address, but modern tracking is more sophisticated, and your IP address is only one part of it. When you log into your Google or Facebook account, that service knows it’s you, regardless of your IP address. Websites also use browser cookies to remember you and track your activity across their pages.
Simple Analogy: Using a VPN is like wearing a mask to the supermarket. The security cameras won’t know who you are. But the moment you use your credit card or loyalty card at the checkout, the store knows exactly who you are and what you bought.
It does not make you 100% anonymous.
For most of us, a VPN provides an excellent level of anonymity from ISPs and data snoops. However, it’s not a cloak of invisibility. With a legal warrant, law enforcement can compel a VPN provider to share information. This is why it is absolutely critical to choose a provider with a strict no-logs policy and a reliable kill switch. If they don’t keep records of your activity, they have nothing to hand over. This is a non-negotiable feature I look for in every VPN I test.
To make it crystal clear, here’s a simple breakdown:
What a VPN protects you from
- Your ISP is seeing your browsing history
- Hackers on public Wi-Fi are intercepting data
- Websites seeing your real IP address and location
- Getting around basic network restrictions
What a VPN does not protect you from
- Viruses and malware on your device
- Phishing scams that trick you
- Tracking cookies from websites
- Being tracked when logged into your accounts
6. FAQ about how does a VPN work
We’ve covered a lot of ground, but you might still have a few specific questions. It’s completely normal. Here are clear, straightforward answers to the most common queries we hear at Safelyo about how VPNs work.
Is using a VPN safe?
Yes, using a reputable VPN is very safe. They use strong, military-grade encryption to protect your data. However, the safety heavily depends on the provider. It’s best to avoid free VPNs that may log and sell your data. Always look for providers with a strict, audited no-logs policy, like the ones Safelyo recommends.
How does a VPN work for dummies?
In the simplest terms, a VPN is an app that hides your online activity. It hides your IP address and puts all your internet traffic into a secret, unbreakable box. This stops your ISP, network administrators, and others from seeing what you do online.
How does a VPN work with wifi?
A VPN works on top of your wifi connection to create a secure connection. When you connect to wifi, the VPN app encrypts all data on your device before it travels over the network. This is especially important on public wifi, as it protects you from anyone on that same network who might be trying to snoop on your activity.
Can you be tracked with a VPN?
It’s much, much harder, but not impossible. A VPN does an excellent job of hiding your IP address and encrypting your traffic, making it very difficult for your ISP or websites to track you. However, things like browser cookies or logging into your Google account can still track your activity on those specific sites. For most people, a VPN provides a very high level of privacy.
Will a VPN slow down my internet?
A small speed loss is normal, but often unnoticeable. This happens because your data has to travel an extra step through the VPN server. However, premium VPNs using modern protocols like WireGuard are so fast that the difference is negligible for everyday browsing, streaming, and even gaming.
Is there a downside to always using a VPN?
For the most part, no. The main drawbacks are a small speed drop and the chance that some sites, including online banking, may block connections from known VPN servers for security reasons. In these rare cases, you may need to temporarily disable your VPN to access the site.
How does a VPN work when traveling internationally?
It makes the internet think you’re still at home. When traveling, you can connect to a VPN server located in your home country. This gives you your home country’s IP address, allowing you to securely access your favorite streaming services, news sites, and even banking apps that might be blocked abroad.
Are VPNs legal?
VPNs are legal in the vast majority of countries, including the U.S., Canada, the UK, and most of Europe. However, a few countries with heavy internet censorship may restrict or ban their use. Using a VPN to perform illegal activities is, of course, still illegal everywhere.
7. Conclusion
Understanding how a VPN works is the first and most crucial step toward taking back control of your digital life and online privacy. It’s not magic; it’s a powerful and accessible tool that creates a secure, private bubble for all your online activities, transforming an open public network into your personal, protected highway.
Now that you’re an expert on how they work, the next step is finding the right one for you. Explore the in-depth guides in the VPN Guides category on Safelyo to choose a trusted service that fits your needs and protects your privacy.