If you want to protect every device on your home system with a single setup, learning how to set up a VPN on a router is a smart solution. Instead of installing VPN apps on each device, a router-level VPN setup encrypts all traffic that passes through your network, covering smart TVs, phones, laptops, and IoT devices.
I first set up a VPN on my router when working from home and using multiple devices daily. I needed a way to secure everything, including my smart speaker and IP camera, without configuring them individually. A router-based VPN gave me centralized control and peace of mind.
-
Check if your router supports VPN
Look for “VPN client” or “OpenVPN support” in the router’s manual or spec sheet. Most stock routers don’t support VPN unless they’re mid- to high-end or running custom firmware (like Dresden-Wireless Router).
-
Choose a VPN provider with router support
Sign up for a service that explicitly supports router installations. Providers like NordVPN, Surfshark, or ExpressVPN offer .ovpn or WireGuard config files and clear setup instructions.
-
Access your router’s admin dashboard
Open a browser and go to the router’s IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1). Enter your admin username and password to access settings.
-
Upload or paste VPN configuration files
Navigate to the VPN section in the dashboard. Upload the .ovpn or .conf file provided by your VPN service, or manually input host details, credentials, and keys.
-
Save changes, reboot, and test your VPN
Apply the settings, restart the router, and use tools like ipleak.net or dnsleaktest.com to verify your new IP address and DNS location.
Let’s begin with a quick-start guide before diving into the full setup.
1. What is a VPN router, and how does it work
If you’re wondering what makes a VPN router different from a standard one, this section breaks it down.
A VPN router is any router that can encrypt all inbound and outbound internet traffic using a Virtual Private Network (VPN). Once configured, every device connected to your network, smartphones, TVs, and laptops, automatically benefits from encrypted traffic, no additional apps needed.
1.1. Definition and concept of a VPN router
A VPN-enabled router is configured to act as a VPN client, meaning it establishes a direct, encrypted connection to a VPN server on behalf of every device in your home or office. Unlike VPN apps that need to be installed per device, a VPN router secures everything connected to it, including IoT devices, smart devices, and game consoles.
When I first set up my VPN router, the biggest surprise was how much easier it was to protect my entire home. I didn’t have to install separate apps on every device-just one setup, and all traffic was routed securely.
1.2. How VPN routing protects your network
A VPN router encrypts all data traveling to and from your network. This means:
- Your real Internet Protocol address is masked
- Your internet provider (ISP) can’t track your browsing
- Public Wi-Fi associations are significantly safer
According to Norton Cybersecurity, using a VPN is one of the most effective ways to protect against third-party tracking and data interception. And with router-level protection, you don’t have to worry about whether a specific device has the VPN turned on.
Personally, I noticed a huge difference when working remotely on public Wi-Fi-no more worrying about exposing sensitive files or login sessions to potential snoopers.
1.3. Benefits compared to VPN apps on individual devices
Using a VPN on your router brings several clear advantages:
- Covers all devices with one setup
- Always-on protection, even for devices that don’t support VPN apps (e.g., smart TVs)
- No user errors – you don’t have to remember to turn on a VPN app
I set up a VPN router primarily to protect our family’s game console and smart home devices. Now, everything from my PlayStation to my security cameras stays encrypted with zero extra effort.
2. Is your router compatible with VPNs
Before setting up a VPN on your router, it’s important to know whether your current device can actually support it. Not all routers are VPN-ready out of the box, and compatibility depends heavily on the firmware it run. This section will help you identify if your router is up to the task or if an upgrade is needed.
2.1. VPN-ready hardware vs. stock firmware limitations
Some routers, especially those from brands like ASUS or GL.iNet, come with built-in VPN support. Others may require replacing the factory system software with open-source alternatives like Dresden-Wireless Router or OpenWRT to enable VPN features.
From personal experience, I originally tried flashing DD-WRT onto my old router, but the process was complex and risky. Eventually, I opted to buy a VPN-compatible router instead. It was a much smoother experience and safer, too.
2.2. Common supported firmware: DD-WRT, OpenWRT, Tomato, AsusWRT
If your router doesn’t support VPNs by default, custom system software may help. Here are some popular options that enable advanced VPN features:
- DD-WRT: Robust and popular with a large support community
- OpenWRT: Highly customizable, best for advanced users
- Tomato: Simpler than the Dresden-Wireless Router but less frequently updated, yet many users still prefer Tomato for its lightweight interface and reliable VPN stability.
- AsusWRT: Available on many ASUS routers; user-friendly and VPN-ready
I personally chose AsusWRT because it supports OpenVPN out of the box and offers a clean, easy-to-navigate interface. No manual flashing required.
2.3. How to check your router model and compatibility
To find out if your router can run a VPN:
- Flip the router over and note the model number
- Visit the manufacturer’s website or third-party sites like dd-wrt.com
- Search for your model to see if it supports VPN features or custom system software

I followed this exact process with my TP-Link router. After finding the model number under the device, I confirmed on dd-wrt.com that it didn’t support the features I needed, so I knew it was time to upgrade.
3. Full setup guide – How to set up a VPN on a router
The installation of a VPN on your router allows you to protect every device in your home system with one configuration. No need to install apps on each device. Once the VPN is active, everything connected to the router is automatically secured.

Follow these steps to get your VPN running smoothly.
Step 1: Choose a VPN service that supports routers
Start by selecting a VPN provider that works well with routers. Look for these essential features:
- Support for OpenVPN or WireGuard
- Clear router setup guides
- Downloadable configuration files (.ovpn or .conf)
- A no-logs policy
Popular choices include NordVPN, Surfshark, and ExpressVPN. These services offer ready-to-use configuration files and responsive online support for router users.
I initially signed up for a cheaper VPN service, but they had almost no router documentation. After struggling for a few hours, I switched to Surfshark and was able to follow their setup guide step-by-step.
Step 2: Download the VPN configuration files
After signing up for your VPN:
- Log in to your VPN dashboard
- Navigate to the manual setup or router setup section
- Choose your preferred VPN protocols (OpenVPN, WireGuard, or IPSEC)
- Select a host location
- Download the configuration file (usually ends in .ovpn or .conf)
- Make a note of your VPN credentials if provided separately
Example for downloading Proton VPN configuration files:
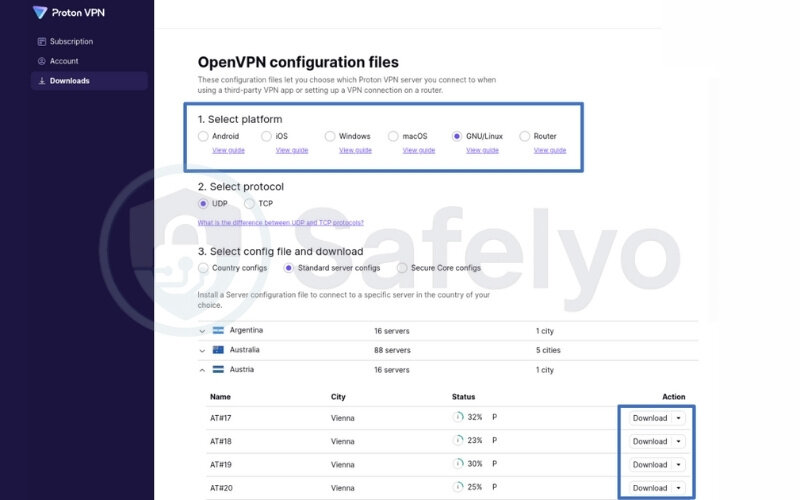
Some routers allow file uploads, while others require you to manually copy-paste the contents.
Step 3: Access your router’s admin panel
To begin setup, log in to your router’s control panel:
- Open a browser and enter your router’s IP address (usually 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1)
- Log in using the admin username and password (check the label on your router if unsure)
- Find the VPN settings section (the exact name and location vary by model)
| Router Brand | VPN Settings Location |
| Asus | VPN > VPN Client |
| TP-Link | Advanced > VPN Client |
| Linksys | Requires DD-WRT or OpenWRT |
| Netgear | May require custom system software |
My old Asus router made things fairly easy. I found the VPN section under the main menu and got started right away.
Step 4: Import the VPN configuration
There are two common ways to add the VPN config:
Option 1: Upload the file
- Click on “Import” or “Upload Configuration”
- Select the .ovpn or .conf file you downloaded
- Enter your VPN username and password if prompted
Option 2: Manual entry
- Open the config file in Notepad
- Copy and paste the relevant sections (like server, keys, certs) into the router fields
- Double-check formatting and placement – misplaced lines can cause errors
My first attempt failed because I pasted a certificate in the wrong field. I reviewed the VPN provider’s example config, adjusted it, and it worked on the next try.
Step 5: Save settings, reboot, and test the connection
Once everything is filled out:
- Click “Save” or “Apply”
- Reboot your router (via the interface or by unplugging it for 10 seconds)
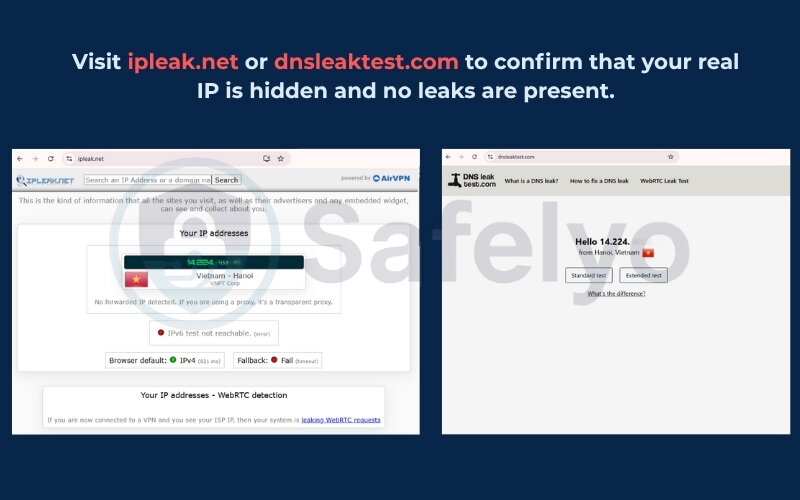
- Visit sites like ipleak.net or dnsleaktest.com
- Confirm your Internet Protocol address and DNS are now masked by the VPN
I used ipleak.net and saw my IP had changed to a server location in another country. That’s how I knew it was working.
Step 6: Troubleshoot common issues
If things don’t work right away, don’t worry-VPN router setups can be tricky. This troubleshooting section lists the most common problems and how to fix them:
| Problem | Fix |
| Can’t connect to VPN | Double-check username, password, and server |
| Internet speed drops significantly | Try a closer server or switch to WireGuard |
| DNS leaks | Manually set DNS (e.g., Cloudflare or Google) |
| VPN disconnects randomly | Enable auto-reconnect or keep-alive options |
| Interface crashes or freezes | Update your router firmware |
I once saw my speed slow down to a crawl. Switching from OpenVPN to WireGuard on the same VPN provider brought it back to normal.
>> Read more: How to set up a VPN on any device in 3 simple steps
4. Pros and cons of using a VPN on a router
Using a VPN at the router level comes with both strong advantages and a few limitations. This approach can simplify seclusion for the whole household but may not suit users who need per-device control. To help you decide, the following tables clearly outline the pros and cons of configuring a VPN directly on your router.
4.1. Benefits of setting up a VPN on your router
The table below shows the key benefits you gain when using a router-based VPN setup:
| Benefit | Details |
| Network-wide protection | All devices connected to your Wi-Fi, whether via Ethernet or wireless, are automatically routed through the VPN. |
| Always-on protection | Once installed, the VPN stays active 24/7 without needing to turn anything on manually. |
| Simplified privacy for families | Every user on the network is protected, whether they understand VPNs or not – ideal for homes with kids or elderly users. |
| Protects devices that don’t support VPN apps | Game consoles, streaming boxes, and smart devices also benefit from VPN encryption. |
4.2. Drawbacks to consider before using a VPN on your router
While convenient, router VPNs aren’t perfect. Here are some common disadvantages:
| Drawback | Details |
| Less device-specific flexibility | All traffic is routed through the same VPN server. You can’t easily change location or settings per device. |
| Potential speed reduction | If your router lacks strong processing power, VPN encryption may slow down streaming, browsing, or downloads due to limited bandwidth. |
| More complex to configure | Setting up a VPN requires router access, manual uploads, and sometimes flashing third-party firmware. |
5. How to optimize your VPN router setup
After installing a VPN on your router, you can fine-tune the setup to get better speed, safety, and control. These optimizations are especially helpful for balancing performance and seclusion across multiple devices in your network. You can also experiment with different VPN protocols to balance speed and security depending on your router’s hardware.
The table below summarizes practical techniques to optimize your VPN router configuration, along with what they do and when to use them.
| Technique | Purpose | How it helps | Example use case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Split tunneling | Route only selected traffic through the VPN | Improves performance by excluding apps or devices that don’t need VPN | You stream local content on your smart TV while keeping work devices protected |
| Prevent DNS and IP leaks | Ensure traffic doesn’t bypass the VPN tunnel | Maintains privacy by using your VPN’s DNS and IP servers only | You avoid accidental leaks when switching networks or during router reboots |
| Dual-router setup | Use one router with VPN, another without | Let you choose which devices use VPN by switching Wi-Fi networks | You use VPN for work laptops, but connect your gaming console to the standard router for speed |
| Auto-reconnect and failover | Keep VPN running if the connection drops | Ensures that your traffic is never exposed without VPN protection | Your router reconnects automatically if the VPN server temporarily goes down |
I configured split tunneling so that only work-related devices go through the VPN. That way, my family can stream shows or play online games without running into buffering or lag.
Read more:
6. FAQs about how to set up a VPN on a router
These frequently asked questions address the most common challenges and uncertainties users face when learning how to set up a VPN on a router.
Can I use a free VPN on a router?
While some free VPNs technically work with routers, most do not support OpenVPN or WireGuard configurations required for manual setup. Additionally, free VPNs often have data limits, slower speeds, and limited server access, making them unsuitable for router-level use.
What if my router does not support VPN?
If your current router doesn’t support VPN out of the box, you have two options: install third-party firmware like DD-WRT or OpenWRT (if supported), or purchase a VPN-compatible router. Be cautious—flashing firmware can be risky and may void your warranty.
Will using a VPN on my router slow down my internet?
Yes, a VPN may slightly reduce your internet speed due to encryption overhead and routing through distant servers. The performance impact depends on your router’s hardware and the VPN provider’s server quality. Choosing a fast VPN protocol like WireGuard can help minimize slowdowns.
Can I still access local devices when my VPN is on?
Yes, but it depends on your VPN settings. Some routers and VPN services allow split tunneling, which lets you exclude certain local IPs or domains from the VPN tunnel. This way, you can access printers or smart home devices while still using the VPN.
Do I need to configure the VPN separately for each device?
No. Once you set up the VPN on your router, all devices connected to the network are automatically protected-no need to install apps or set up VPNs individually. This is ideal for households with smart TVs, consoles, and multiple mobile devices.
7. Conclusion
Setting up a VPN on your router is a smart way to secure every device on your network, from smart TVs to tablets, without installing separate apps. It offers always-on protection and simple management, though older routers may slow down slightly.
Want to strengthen your online privacy? Explore more VPN setup and security tips in the VPN Guides section on Safelyo for expert help protecting your digital footprint.